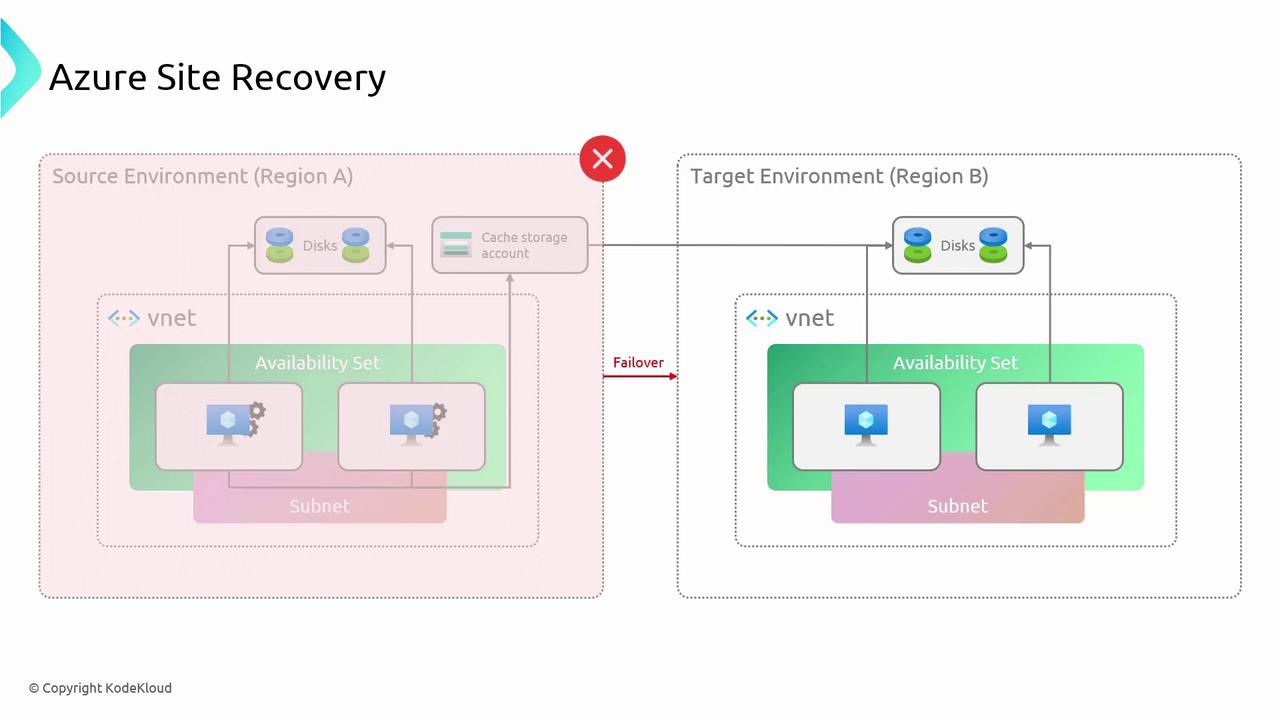
ASR not only facilitates disaster recovery but can also be automated using REST APIs, health metrics, and load balancing solutions such as Azure Traffic Manager.
Configuring Disaster Recovery via the Azure Portal
In this section, we walk through configuring disaster recovery for a virtual machine named “RSV Demo 1” running IIS on a Windows server.- Access the Virtual Machine Details Open the virtual machine details page in the Azure portal.
- Initiate Disaster Recovery Setup Click on the disaster recovery option. You can create a Recovery Services vault during this process. For this demonstration, review the disaster recovery map and settings.
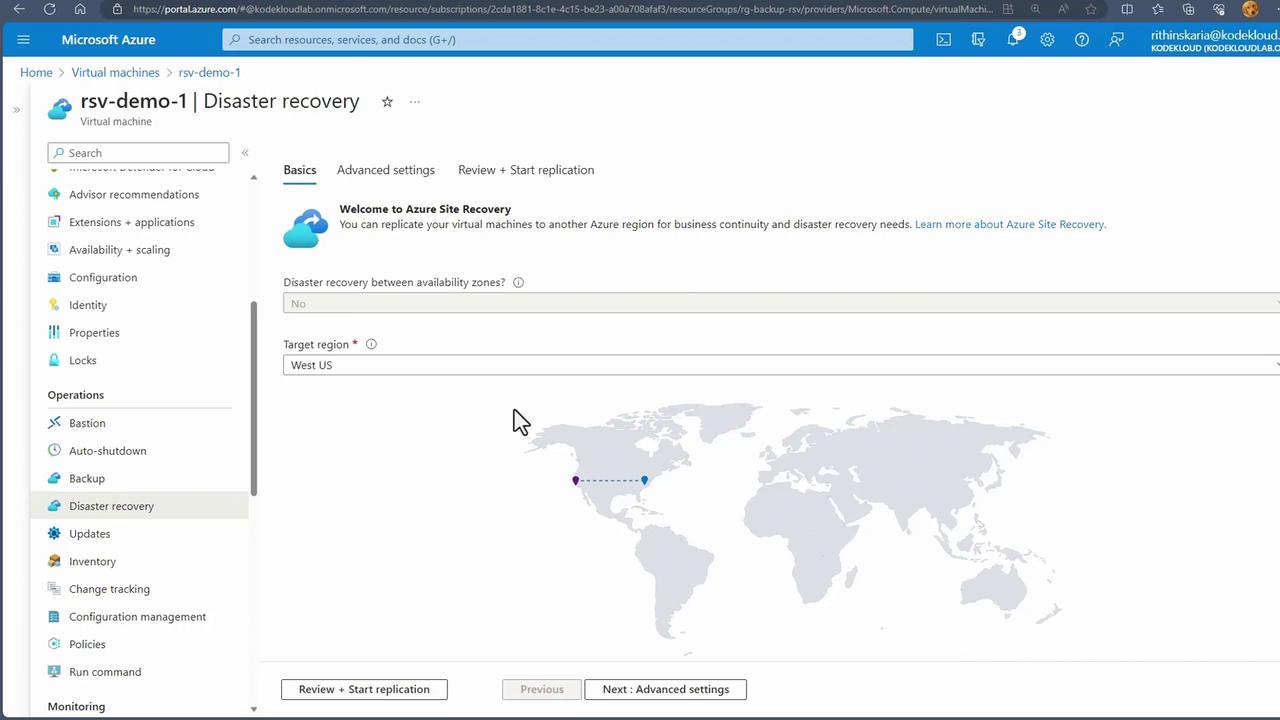
- Select the Target Region Choose a target region—for example, West US if the source is located in East US. In the advanced settings, Azure creates the necessary infrastructure (resource groups, virtual networks, and availability sets) in the target region. The target resource group may be annotated with an “ASR” suffix (e.g., “RG Backup RSV ASR”).
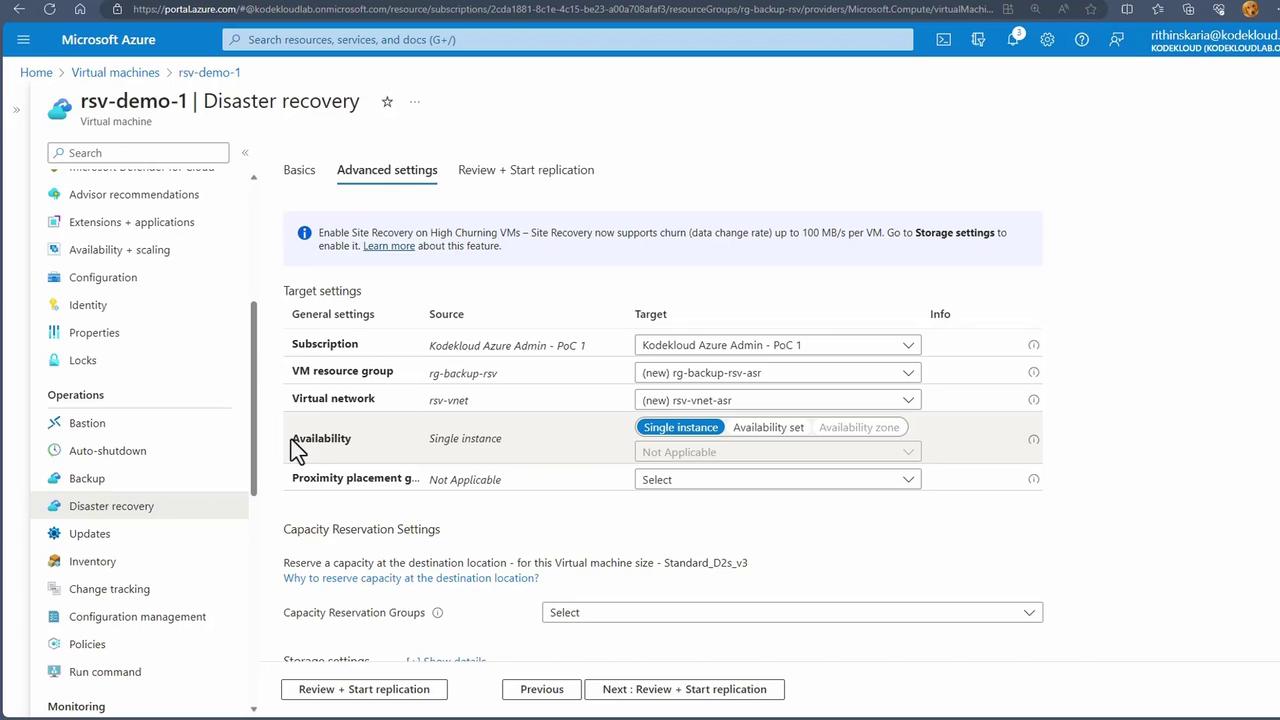
- Review and Configure Replication Settings Examine the storage options, replication settings, and extension management. Storage settings define the cache storage account. Replication options let you choose the recovery services vault, vault resource group, and replication policy. Extension settings manage the ASR extension on the virtual machine.
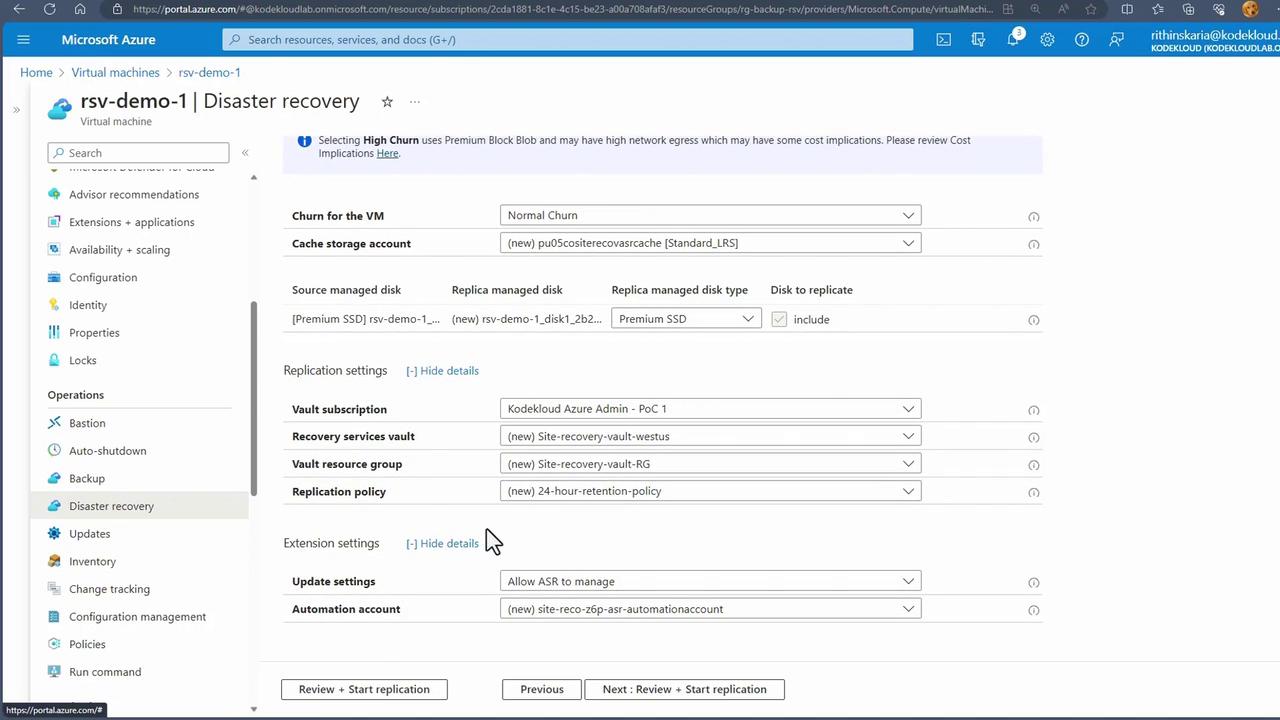
- Start Replication Click “Review and Start Replication” to see details such as the source disk, replica disk (configured as premium SSD), and cache storage account. Confirm by clicking “Start Replication” to trigger the creation of resources in West US. The replication of data to the target region will commence once the resources are provisioned.
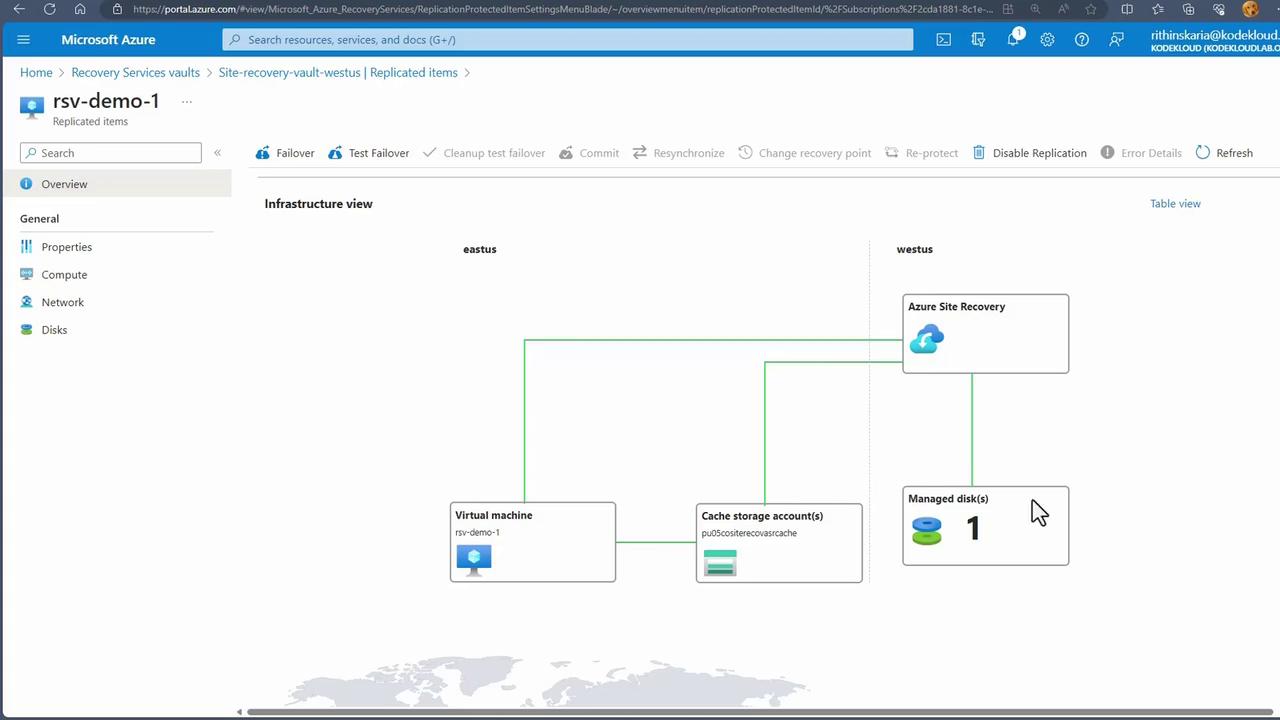
Performing a Test Failover
Conducting a test failover validates that your disaster recovery setup functions correctly without affecting your production environment.- Initiate the Test Failover In the Azure portal, select the test failover option.
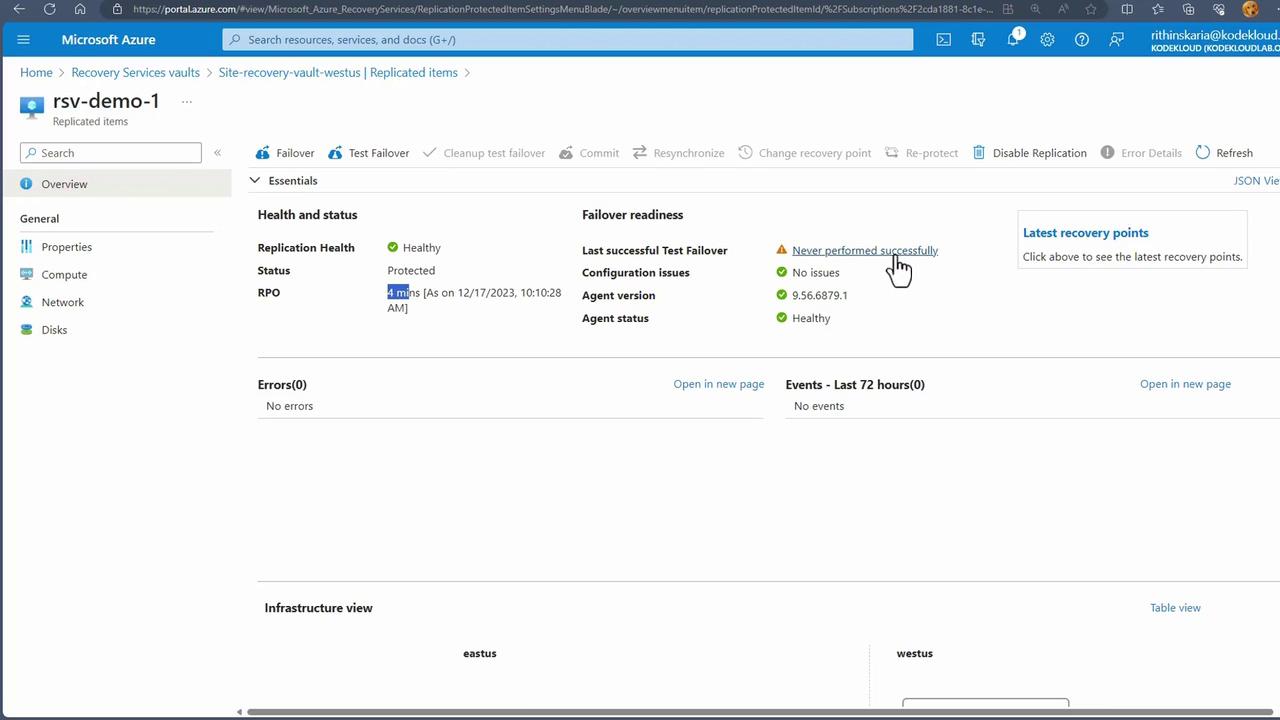
-
Configure Test Failover Settings
- Choose the source region (e.g., East US) and the destination (e.g., West US).
- Select the appropriate recovery point; typically, the latest recovery point with application consistency is recommended.
- Pick the ASR virtual network that was created during the initial setup.
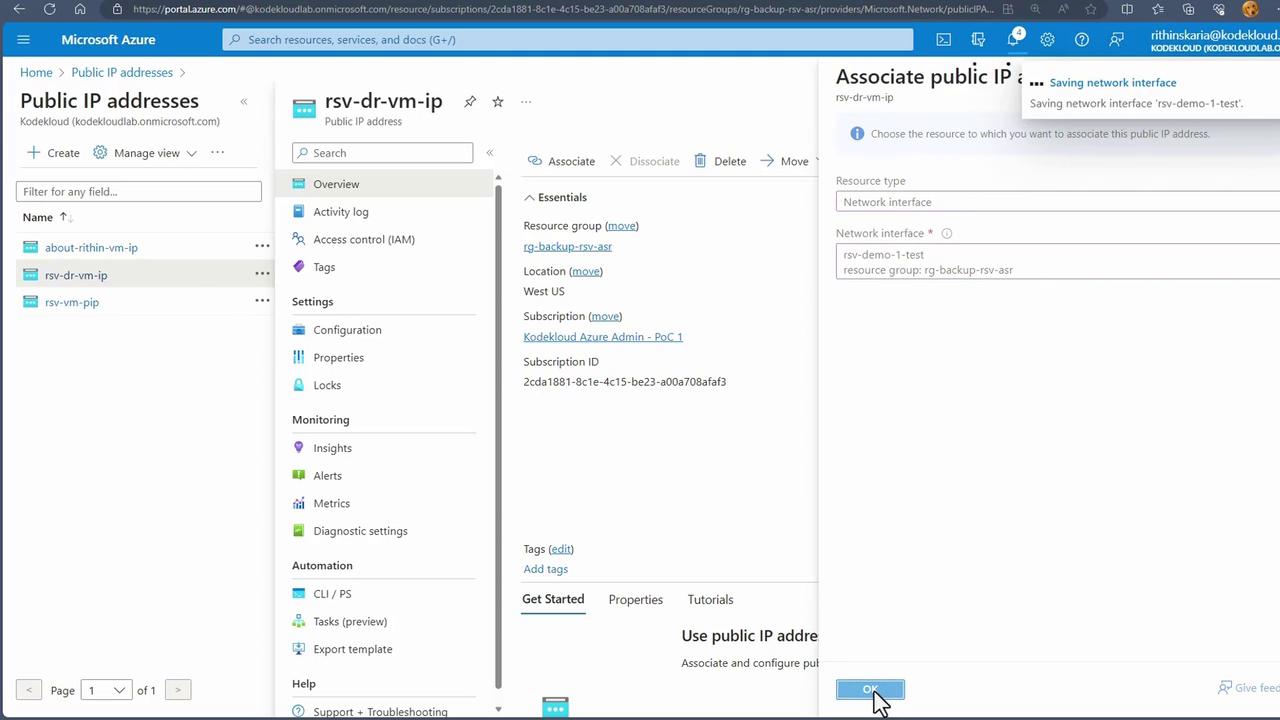
- Provisioning a Temporary Virtual Machine The test failover process creates a temporary virtual machine in the target region, attaching the relevant managed disk. To ensure connectivity, a public IP address must be available. Since this is not created automatically, you need to create a new public IP.
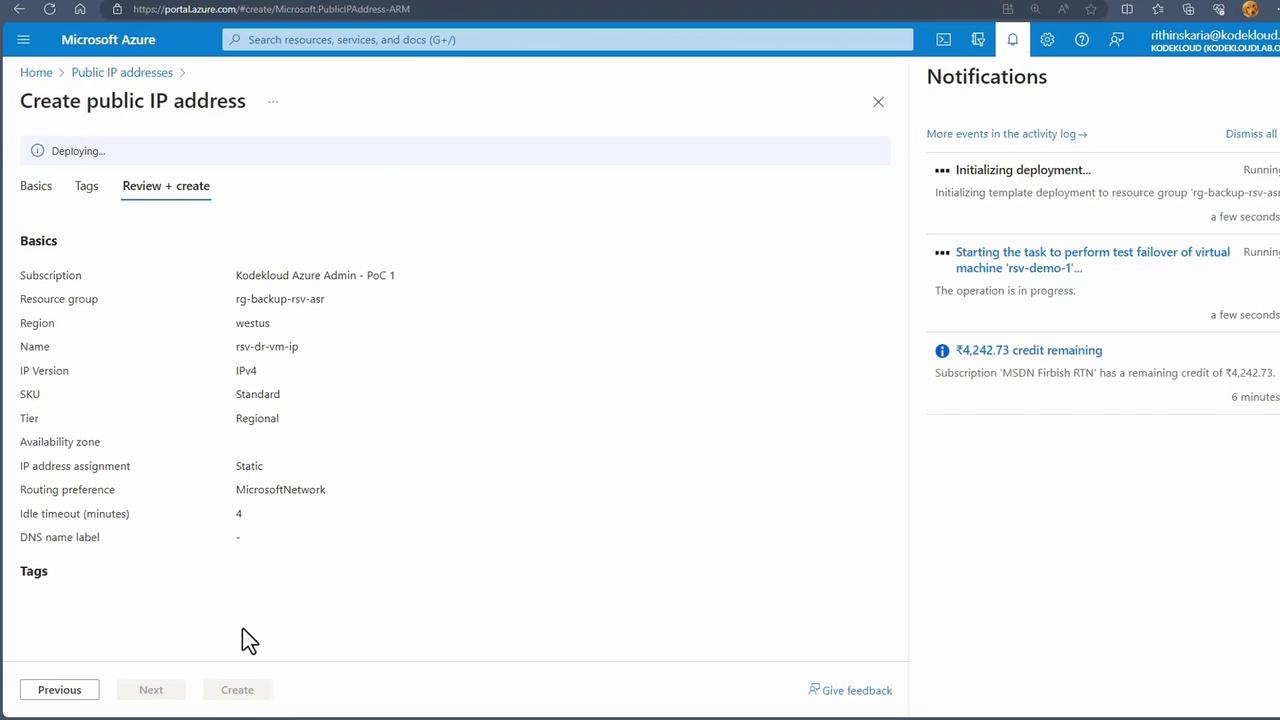
- Verify the Test VM Deployment After the virtual machine starts, monitor its status in the virtual machines list.
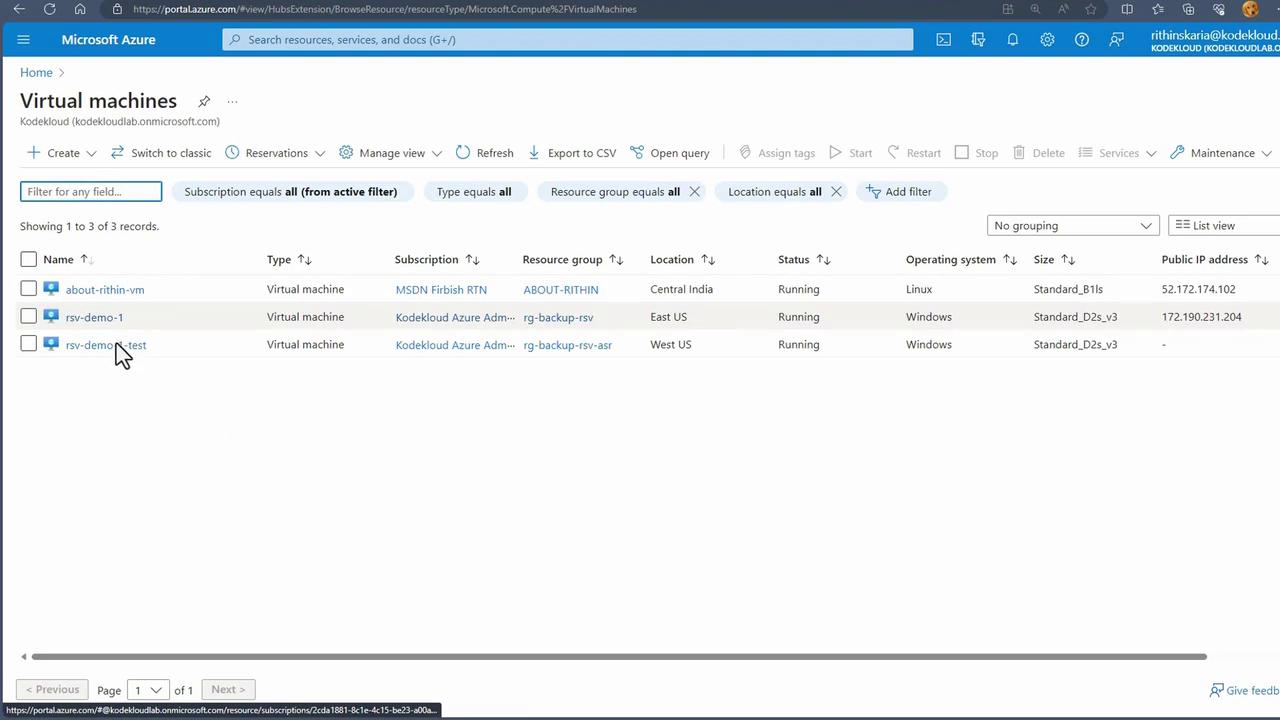
-
Set Up Network Connectivity
If no Network Security Group (NSG) is attached to the test VM, proceed as follows:
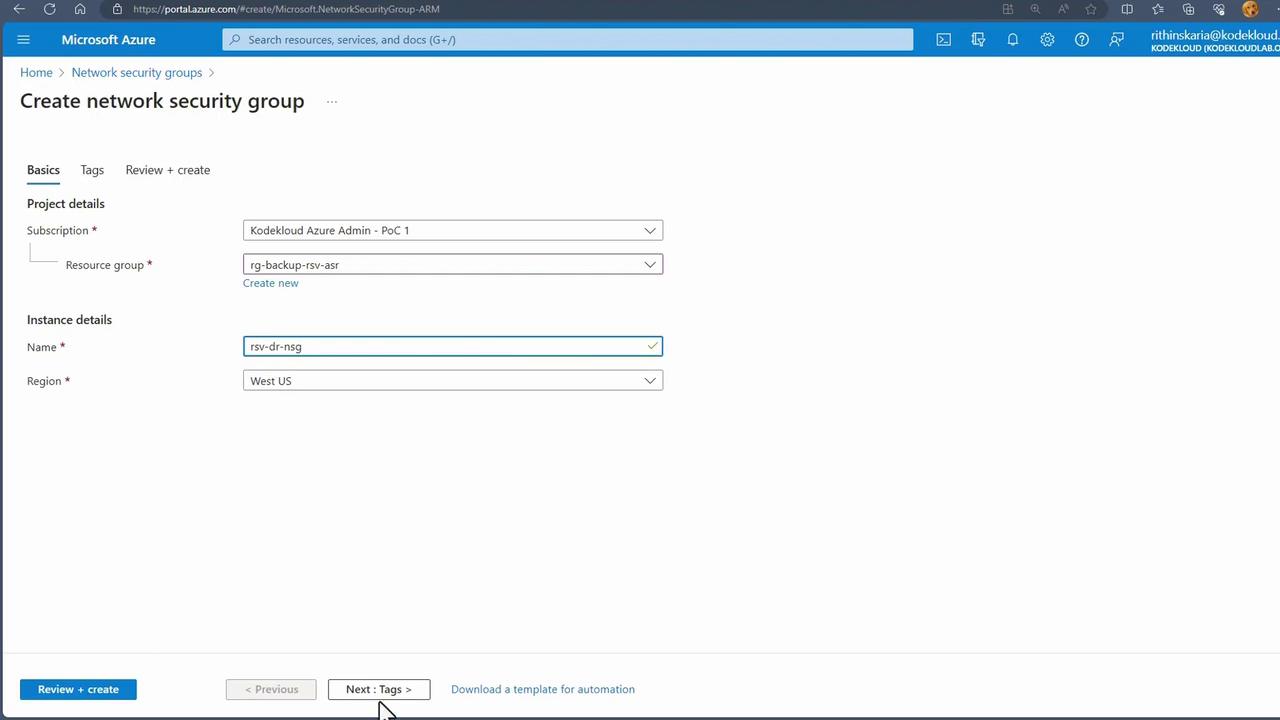
- Create an NSG in the ASR resource group.
- Add inbound security rules for required ports (e.g., TCP ports 80 and 3389).
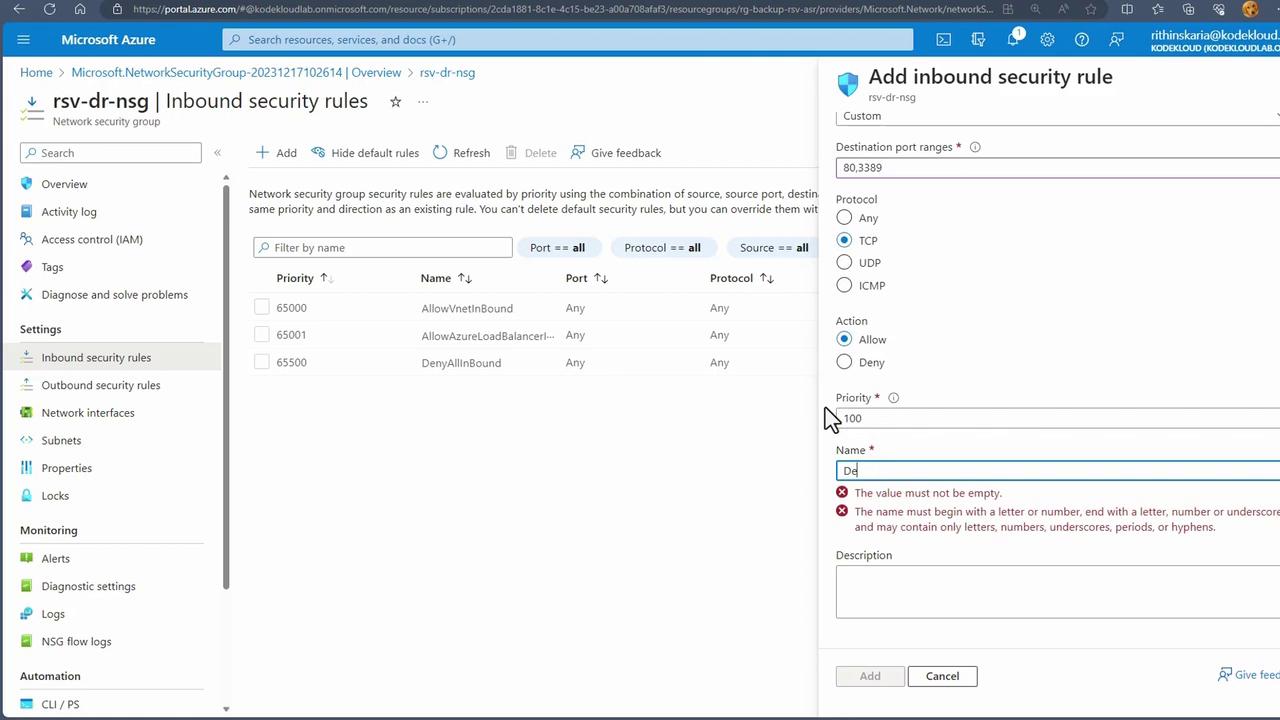
-
Associate NSG and Public IP
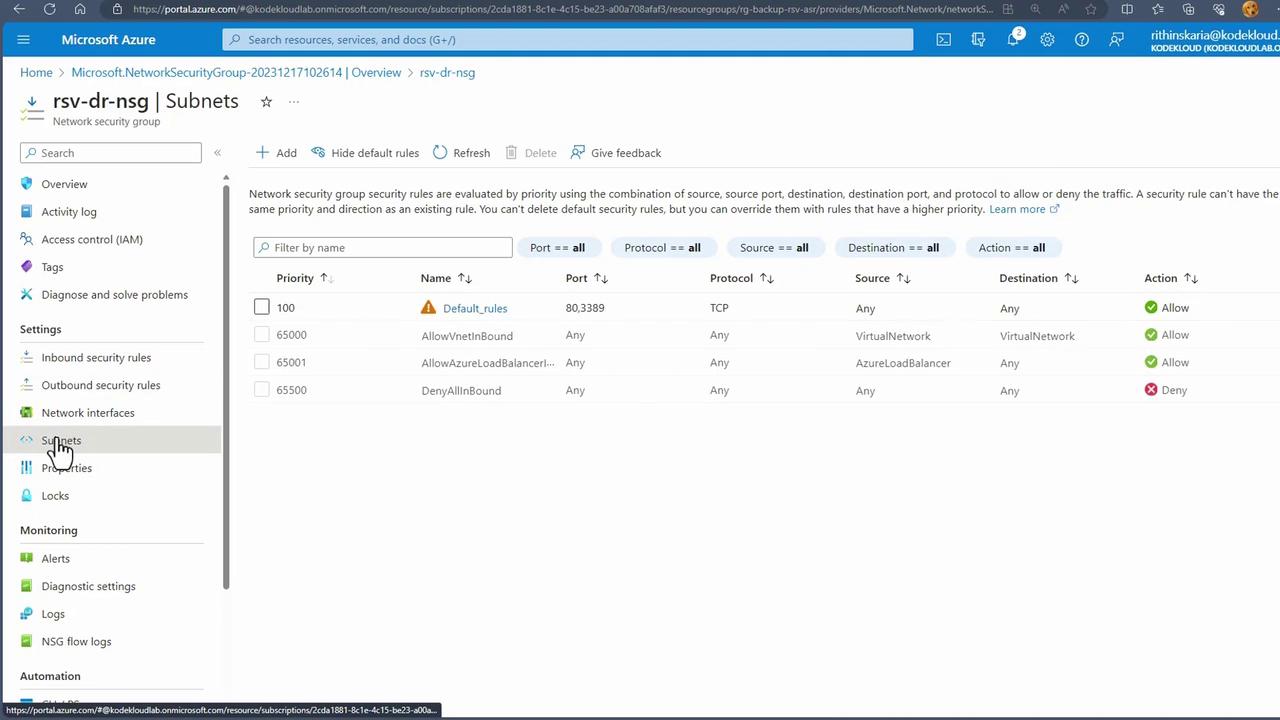
- Associate the NSG with the DR subnet so that any VM in the subnet inherits the security rules.
- Finally, associate the newly created public IP address with the test VM’s network interface.
- Verify the Test Failover Access the public IP address via a browser. If you see the IIS page (identical to production), the test failover is confirmed successful.
A test failover does not impact your production environment. It enables you to validate that all systems, from network connectivity to replication accuracy, are functioning as expected.
Completing the Disaster Recovery Test
After a successful test failover, it is essential to clean up the test environment:- Navigate to the replicated items in the Azure portal.
- Select “Clean Up Test Failover Pending” to remove the test configurations.
- Confirm by deleting the test virtual machine when prompted.