DevOps Pipeline at a Glance
| Stage | Objective | Key Tools | Trigger |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Integration | Build, test, and secure code | npm, Jest, SonarCloud, Docker, Snyk | Push to feature branch |
| Continuous Deployment | Deploy container to AWS EC2 | SSH, Docker CLI | Image pushed to registry |
| Continuous Delivery | GitOps-driven rollout to Kubernetes and Lambda | Argo CD, OWASP ZAP, AWS CLI | Pull request creation & merge |
| Post-Build | Collect reports and notify stakeholders | Jenkins archiving, AWS S3, Slack webhook | Completion of all stages |
1. Continuous Integration (CI)
When Jenkins detects a push to a feature branch, it executes the following pipeline. Any failure halts progress early, ensuring only high-quality code advances.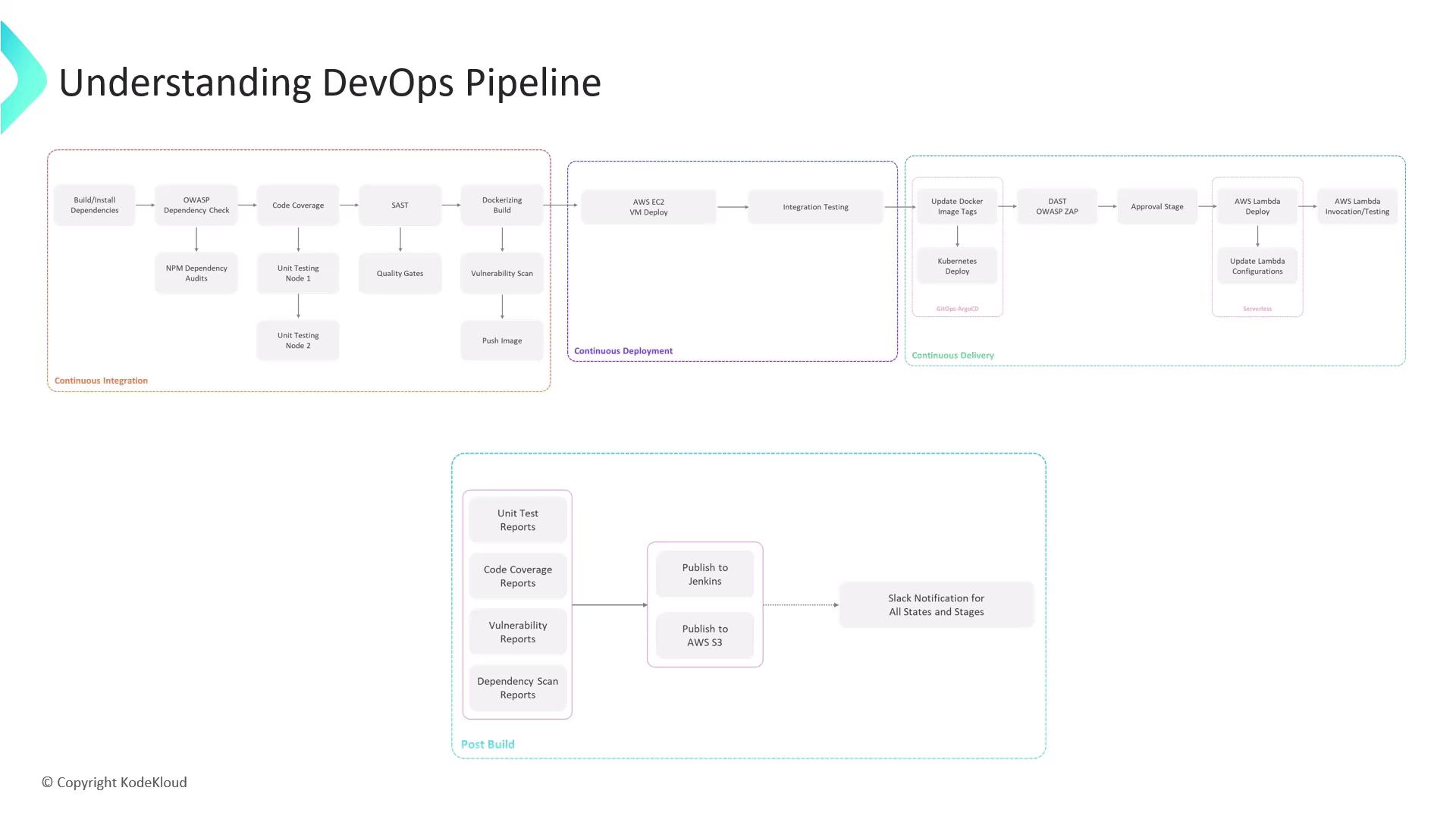
1.1 Install Dependencies
Install Node.js project packages:1.2 Dependency Vulnerability Checks
Scan for known vulnerabilities:1.3 Unit Tests & Coverage
Run unit tests and generate coverage reports:1.4 Static Code Analysis
Analyze code quality with SonarCloud and enforce a quality gate.If the SonarCloud quality gate fails, the Jenkins build is marked as failed. Address all blockers before proceeding.
1.5 Containerization
Package the application into a Docker image:1.6 Image Vulnerability Scan
Use Snyk to scan the container:1.7 Push to Container Registry
On success, push the image to your registry (e.g., Docker Hub or AWS ECR):2. Continuous Deployment (CD)
Once the image is available in the registry, deploy and test on AWS EC2.-
Deploy the Docker container on an EC2 instance:
- Execute integration tests to validate endpoints.
-
Create a pull request (PR) from your feature branch to
main—this triggers the continuous delivery pipeline.
3. Continuous Delivery
A GitOps-driven rollout ensures your changes propagate safely to production-like environments.- Update Kubernetes manifests with the new image tag.
- Let Argo CD sync the cluster automatically.
- Run Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) using OWASP ZAP.
- Peer review and merge the PR.
- A manual approval step in Jenkins authorizes the final deployment.
A designated approver must review security and compliance reports before deploying to production.
- Deploy updated Lambda functions:
- Verify the Lambda endpoints:
4. Post-Build
After deployments complete, gather and publish artifacts:- Archive test results, coverage, and vulnerability reports in Jenkins.
-
Upload to Amazon S3 for audit and compliance:
- Notify your team via Slack webhook.
This pipeline showcases Jenkins’ flexibility across EC2, Kubernetes, and Lambda environments, integrating security, testing, and delivery best practices from code commit to production.