Why GitOps?
- Git-Centric Control
Every change is performed via Git commits and pull requests. - Declarative Desired State
Infrastructure and applications are described in code, making the system reproducible. - Automated Reconciliation
A GitOps operator constantly syncs the live cluster state with the Git repository.
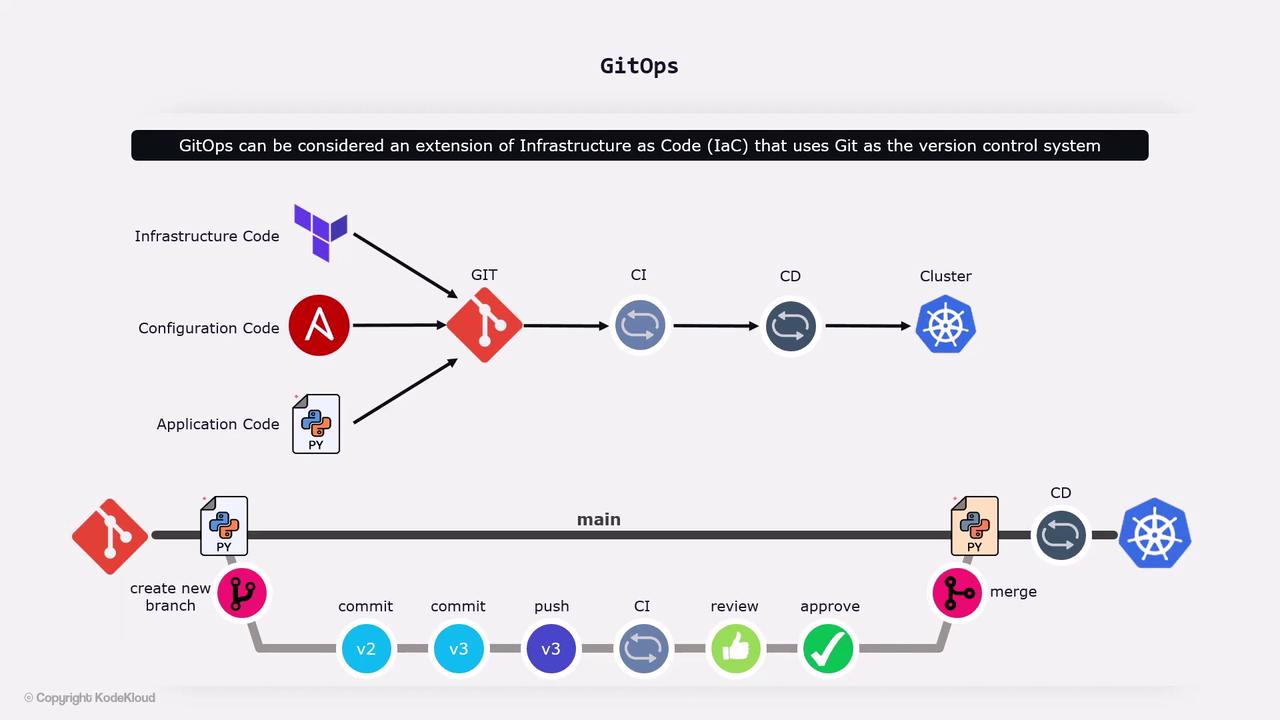
- Declarative Configuration
Store all infrastructure, application manifests, and configuration files in Git. - Versioned and Immutable
Every change is tracked. Roll back by reverting to a previous commit. - Automated Delivery Pipeline
A GitOps operator inside your Kubernetes cluster watches Git for updates. - Continuous Reconciliation
Drift detection ensures the live environment matches the desired state.
Developer Workflow
- Create a feature branch from
main. - Update application code or Kubernetes manifests.
- Open a pull request for review.
- After approval, merge back into the central repository.
CI/CD Integration
A CI system automatically:- Runs unit and integration tests.
- Builds a Docker image and pushes it to a container registry.
- Updates the Kubernetes manifests in your Git repository.
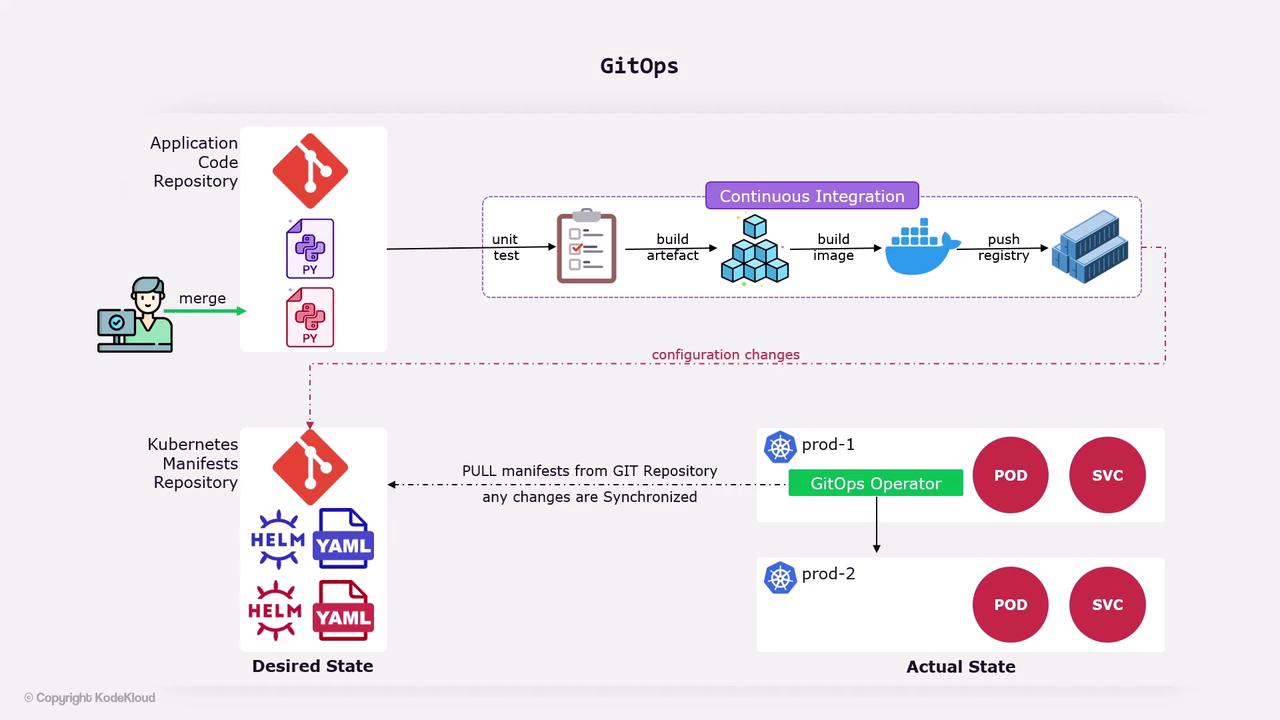
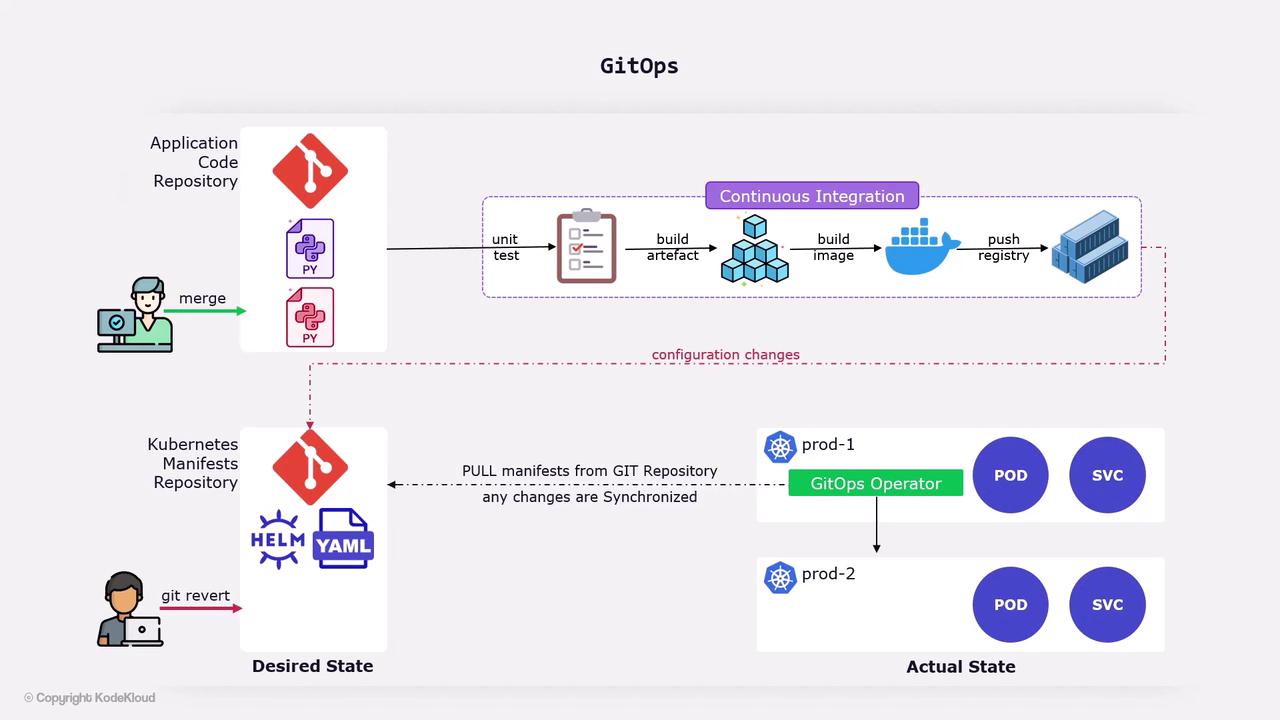
GitOps Operator Workflow
- The operator polls (or listens for webhooks) on your Git repository.
- Detects changes in manifests or configs.
- Applies updates to your Kubernetes cluster (or clusters).
- Continuously monitors live state and reconciles any drift.
| Component | Purpose | Example Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Git Repository | Single source of truth for code and configs | GitHub, GitLab |
| GitOps Operator | Syncs Git state to the cluster | Argo CD, Flux |
| CI System | Builds, tests, and packages applications | Jenkins, GitHub Actions |
| Container Registry | Stores Docker images | Docker Hub, ECR |
| Kubernetes Cluster | Runs and orchestrates workloads | EKS, GKE, AKS |
GitOps operators typically reconcile every few seconds. If you manually change resources in your cluster, the operator will revert them to match the Git state.