In this tutorial, we’ll manually deploy a Node.js Express application to AWS Lambda. You will learn how to prepare your code, package it, upload to S3, and update the Lambda function. Afterwards, we’ll automate these steps using a Jenkins pipeline.
AWS Resources Setup First, ensure you have an Amazon S3 bucket and an existing AWS Lambda function.
Lambda Function Overview Parameter Value Name solar-system-functionPackage type zipRuntime Node.js 20.x Handler app.handler
Environment Variables By default, MongoDB credentials are hardcoded. We’ll remove them when automating the pipeline.
Avoid storing sensitive credentials in plain text. Use AWS Secrets Manager or secure environment variables.
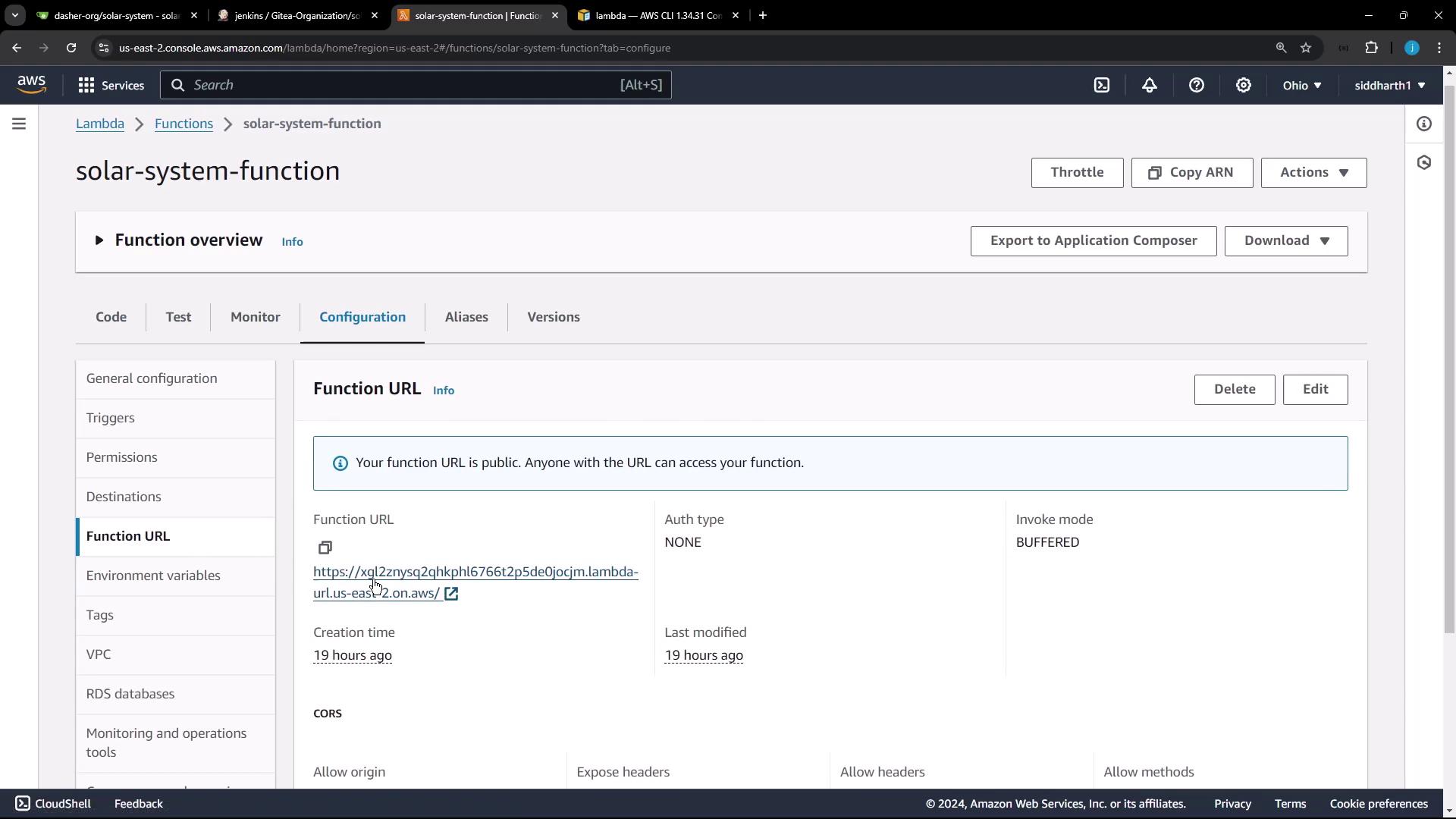
Function URL and Application Version This Lambda function has a public URL serving version 3.0 of the Solar System app.
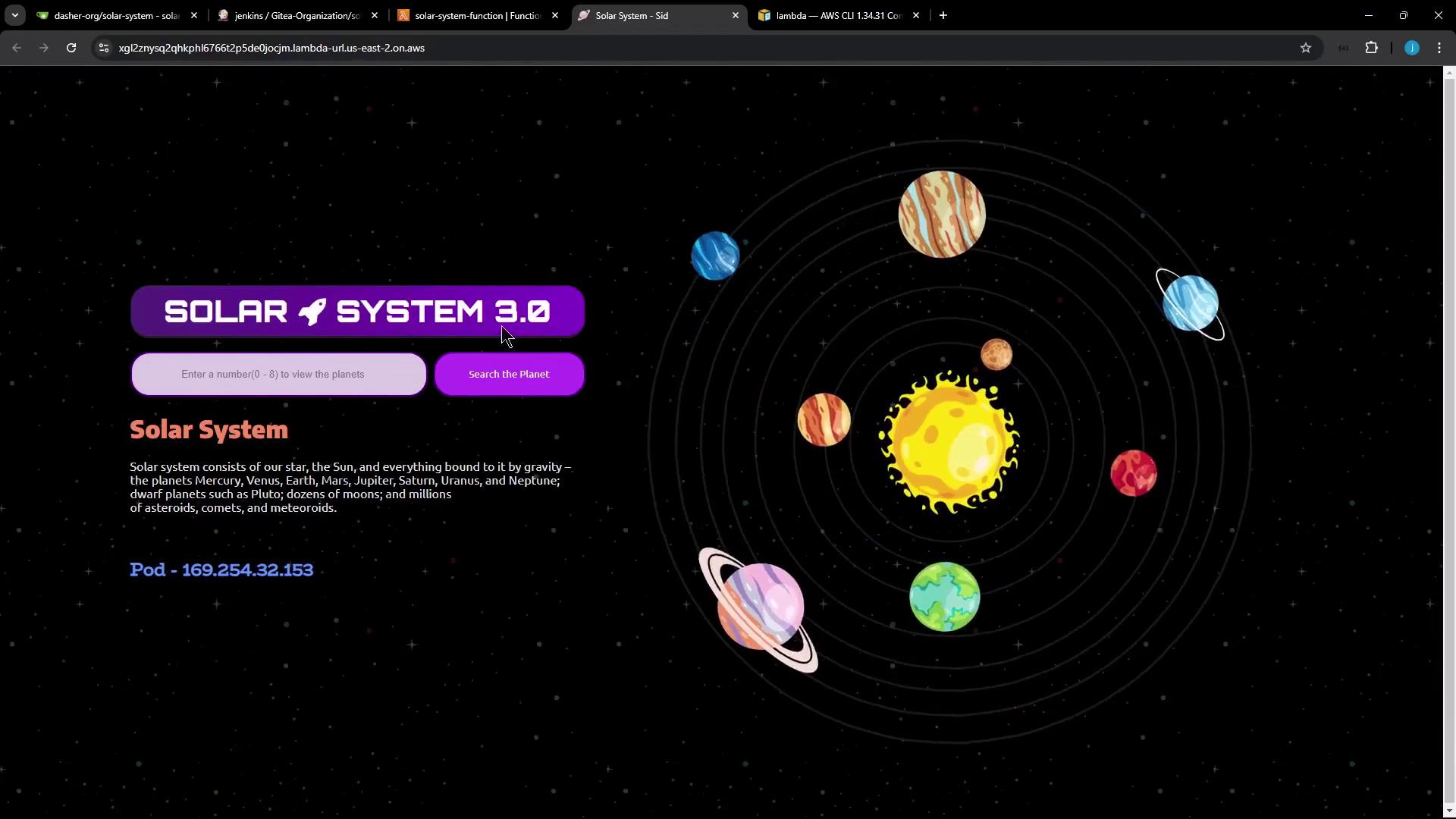
Visit the URL to view your app:
CORS is enabled (*) for public access.
Manual Deployment Steps Follow these steps to deploy your app:
Clone the repository.
Adapt app.js for AWS Lambda.
Install dependencies.
Update index.html version.
Package the application.
Upload the ZIP to S3.
Update Lambda function code.
Verify the deployment.
1. Clone the Repository mkdir sandbox && cd sandbox git clone https://gitlab.com/sidd-harth/solar-system.git cd solar-system
Replace the Express listener with a Serverless handler.
Original at the end of app.js:
app . listen ( 3000 , () => { console . log ( "Server running on port 3000" ); }); module . exports = app ;
Run these commands:
sed -i 's|app.listen(3000.*|//&|' app.js sed -i 's|module.exports = app;|// module.exports = app;|' app.js echo -e "\nmodule.exports.handler = require('serverless-http')(app);" >> app.js
The final lines should read:
// app.listen(3000, () => { console.log("Server running on port 3000"); }); // module.exports = app; module . exports . handler = require ( 'serverless-http' )( app );
3. Install Dependencies Ensure serverless-http is listed in package.json:
{ "dependencies" : { "cors" : "2.8.5" , "express" : "4.18.2" , "mongoose" : "5.13.20" , "serverless-http" : "^3.2.0" } }
Install with npm:
4. Update Application Version Change Solar System 3.0 to Solar System 4.0:
sed -i 's/Solar System 3.0/Solar System 4.0/' index.html
5. Package the Application Create the deployment ZIP:
zip -qr solar-system-lambda.zip app.js package.json package-lock.json index.html node_modules
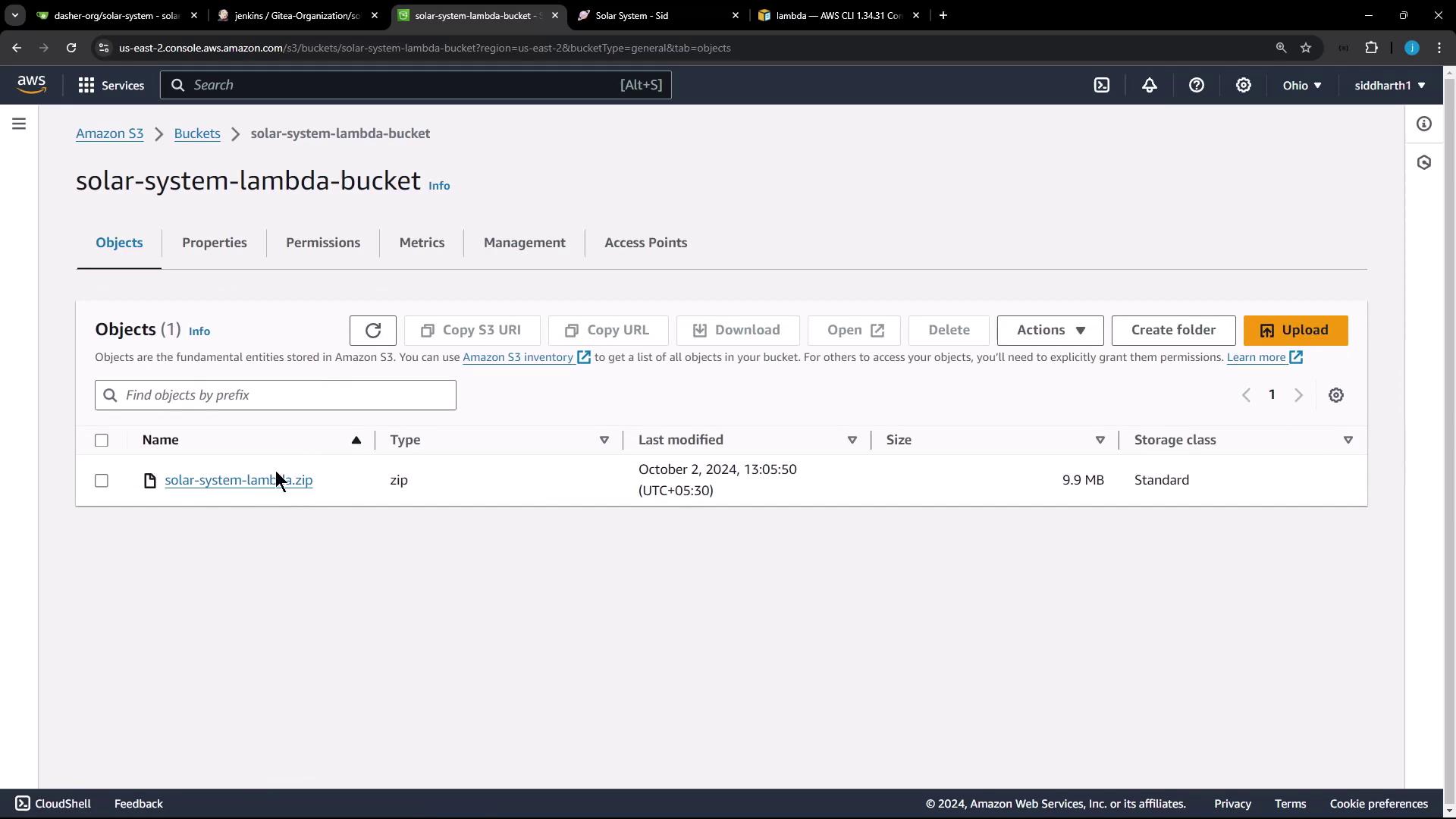
6. Upload the ZIP to S3 Upload to your Lambda bucket:
aws s3 cp solar-system-lambda.zip s3://solar-system-lambda-bucket/solar-system-lambda.zip
Confirm in the S3 console:
7. Update Lambda Function Code Point your Lambda to the new S3 object:
aws lambda update-function-code \ --function-name solar-system-function \ --s3-bucket solar-system-lambda-bucket \ --s3-key solar-system-lambda.zip
Optionally, view current configuration:
aws lambda get-function-url-config --function-name solar-system-function
Sample Output { "FunctionName" : "solar-system-function" , "Runtime" : "nodejs20.x" , "Handler" : "app.handler" , "LastModified" : "2024-10-07T12:36:54.000+0000" , "Version" : "$LATEST" }
8. Verify the Deployment Retrieve the function URL:
aws lambda get-function-url-config --function-name solar-system-function
Example:
{ "FunctionUrl" : "https://kg12znysq2qhk1676t2p5de0jcm.lambda-url.us-east-2.on.aws/" , "AuthType" : "NONE" , "Cors" : { "AllowOrigins" : [ "*" ] } }
Open the URL and confirm it shows Solar System 4.0 .
Summary
Replace app.listen with a serverless-http handler.
Run npm install.
Update the version in index.html.
Zip the application files.
Upload the ZIP to S3.
Execute aws lambda update-function-code.
Validate the new version via the function URL.
Next, we’ll automate this workflow in a Jenkins pipeline.
Links and References