Common Plugin Categories
| Category | Purpose | Example Plugins |
|---|---|---|
| Source Control Management | Integrate with Git providers | Git, GitHub Branch Source |
| Build Tools | Automate builds with popular frameworks | Maven Integration, Gradle Plugin |
| Quality & Security | Perform static analysis, code coverage, and vulnerability scans | SonarQube Scanner, OWASP Dependency-Check |
| Notifications | Send build and deployment alerts | Slack Notification, Email Extension |
| Cloud Integrations | Manage resources on public clouds | AWS Steps, Google Cloud Build |
| Distributed Builds | Scale workloads across multiple agents | Distributed Builds Plugin, Swarm Plugin |
How Plugins Are Packaged
Jenkins plugins are distributed as JAR archives with.hpi (legacy) or .jpi (modern) extensions. Each package contains:
- Plugin code (Java/Groovy classes)
- Static resources (JavaScript, CSS)
- Metadata (
pom.xml,plugin.xml)
.jpi and .hpi versions are present.
Installing Plugins
When you set up Jenkins for the first time, choose one of the following:- Install Suggested Plugins
- Select Plugins Manually
Choosing Install Suggested Plugins provides a curated set of essential plugins, making it ideal for newcomers.
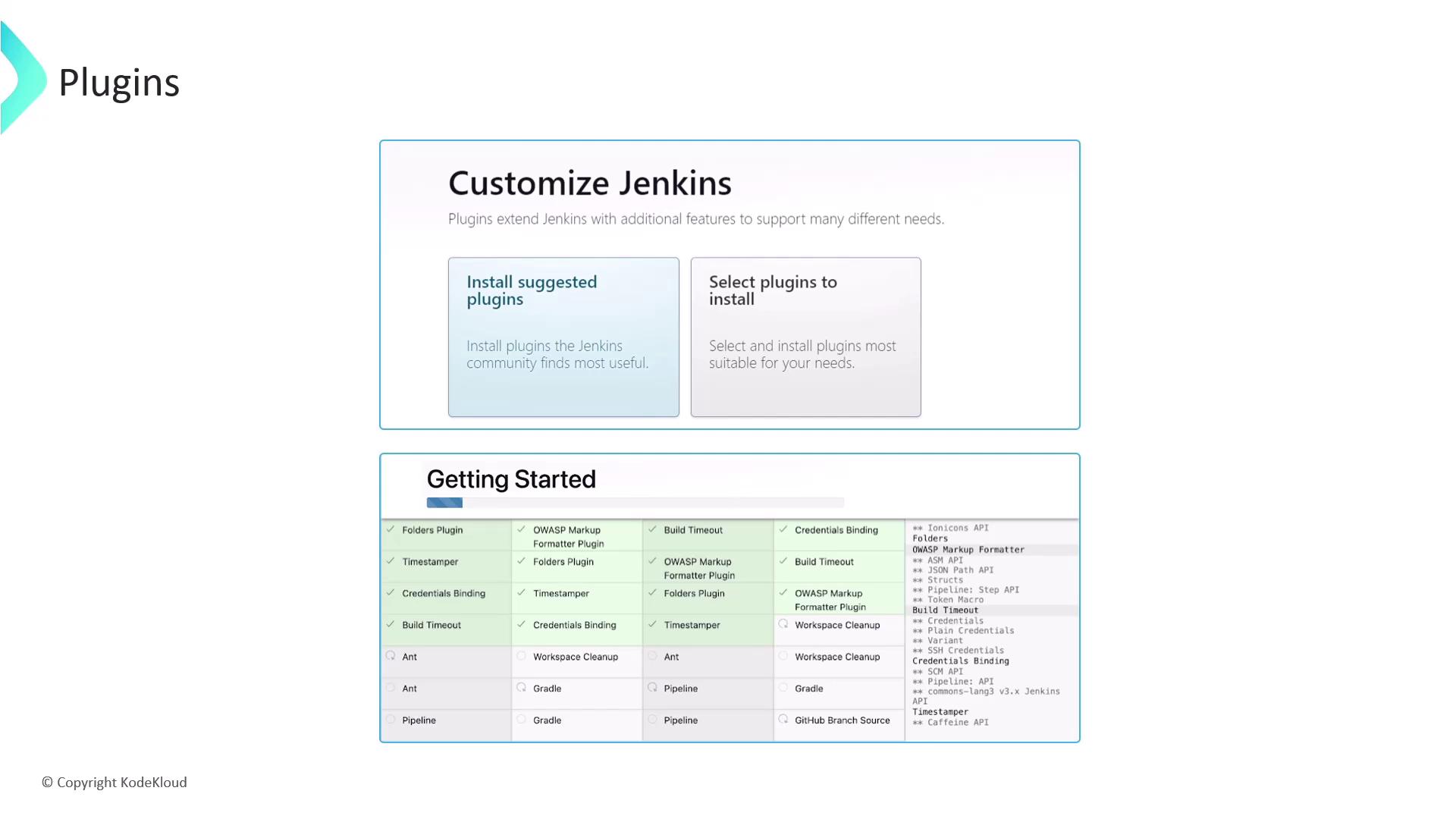
Recommended Starter Plugins
- Git Integration
- Pipeline (Workflow)
- Maven Integration
- Gradle Plugin
- Docker Pipeline
Managing Installed Plugins
After installation, head to Manage Jenkins ➔ Manage Plugins to enable, disable, update, or uninstall extensions.Removing a plugin can break dependent functionality. Always verify plugin dependencies before uninstalling.
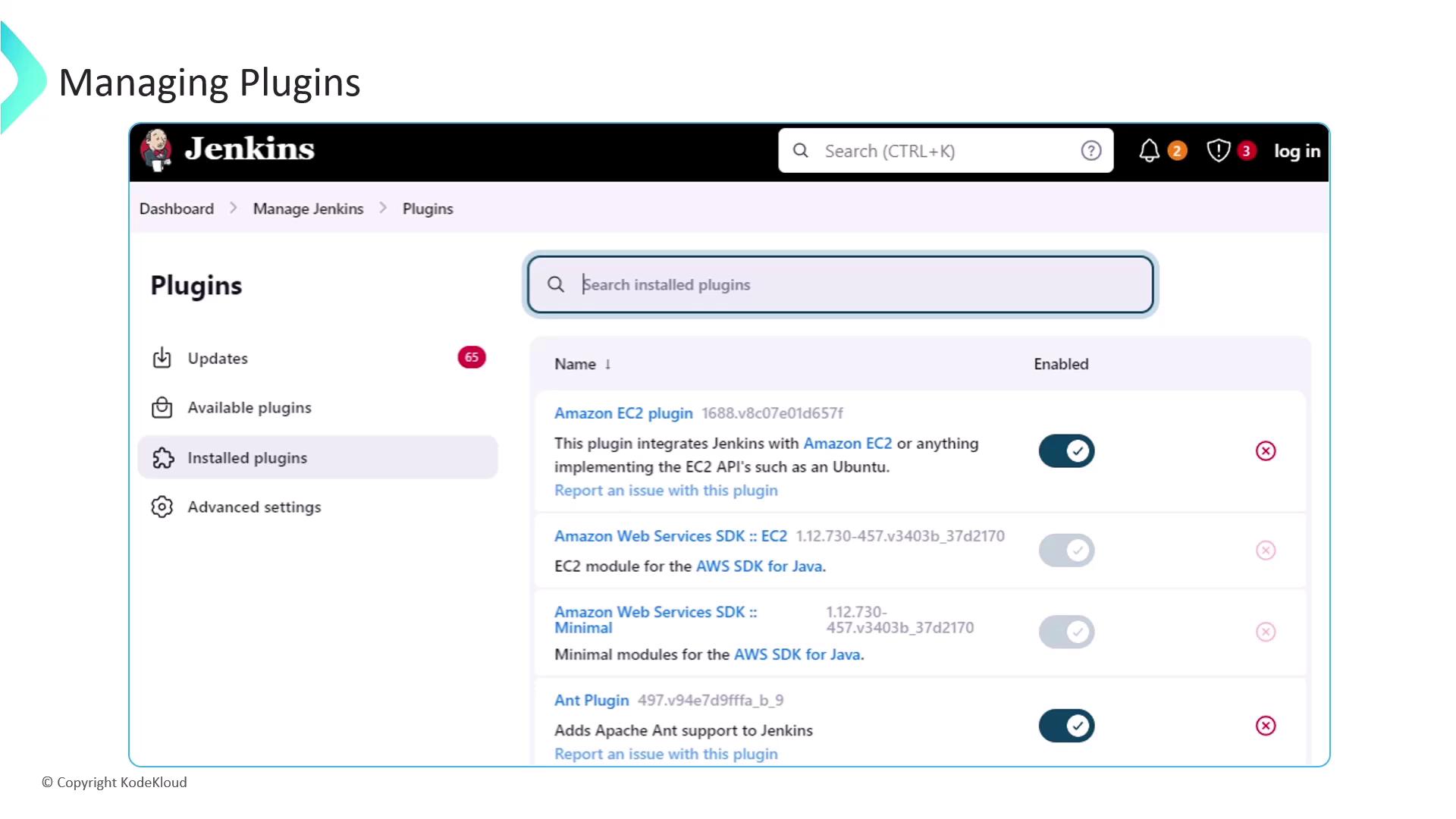
Plugin Update Center
The Updates tab shows available plugin updates. Regularly update to benefit from new features and security fixes.Next Steps
- Automate plugin installation via Jenkins Configuration as Code
- Explore advanced plugins (Blue Ocean, Kubernetes, Terraform)
- Integrate with external security scanners and compliance tools