- Clone and migrate a Kubernetes manifest repository.
- Create and encrypt MongoDB credentials with Bitnami Sealed Secrets.
- Deploy a Solar System application using Argo CD in a secure GitOps workflow.
1. Clone the Manifest Repository
Start by cloning the repository that holds your Kubernetes manifests:mongo-db-creds, which you’ll create in the next sections.
2. Migrate to Your Git Host
If you need to host your manifests elsewhere (for example, Gitea or another GitHub organization), use your Git provider’s import or migration tools: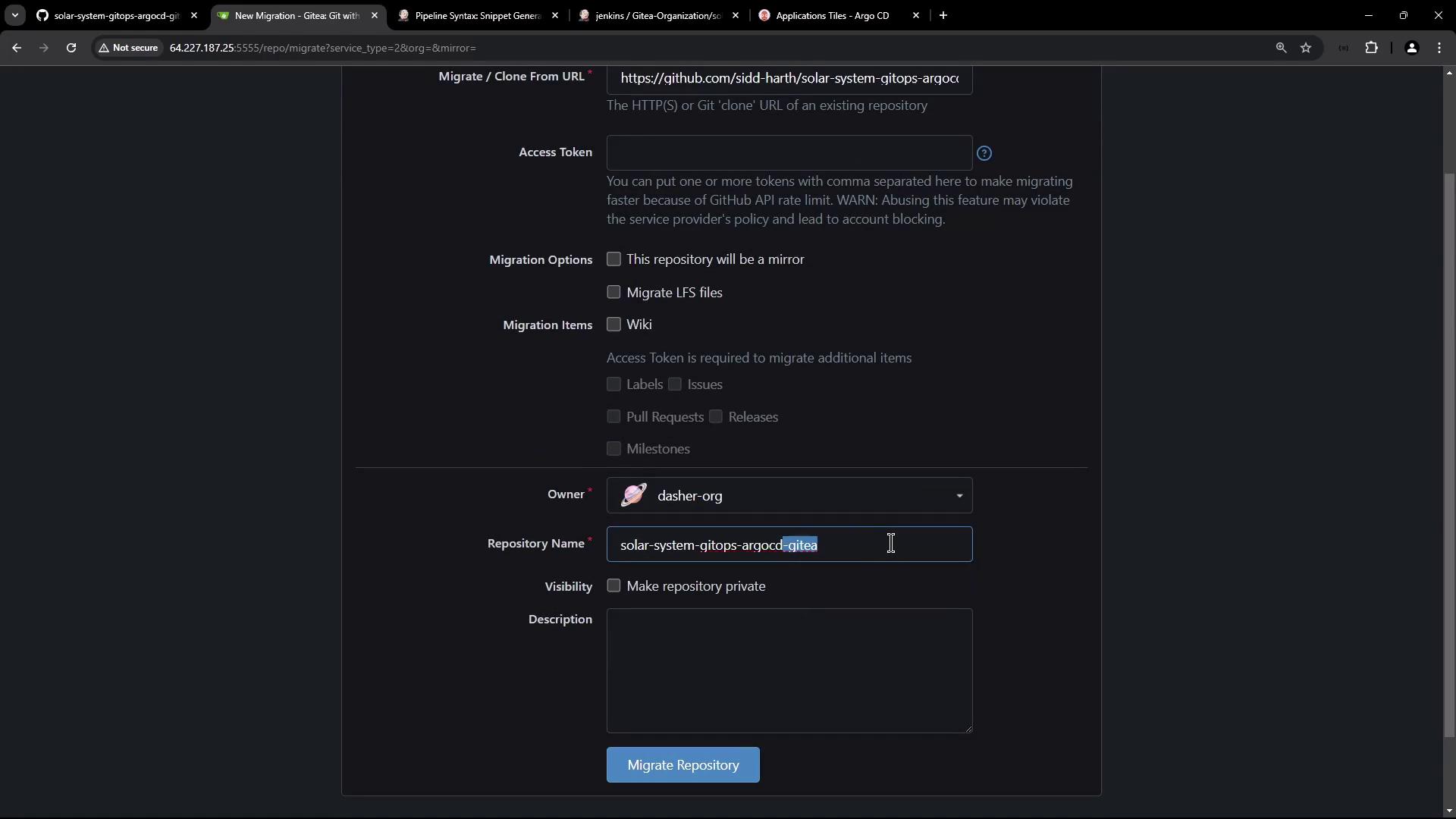
kubernetes/deployment.yaml and kubernetes/service.yaml are present in your new repository.
3. Create the MongoDB Secret
Verify your Kubernetes cluster context and namespaces:Do not commit raw secrets to Git. Use an encryption mechanism like Bitnami Sealed Secrets to secure your credentials.
4. Seal the Secret with Bitnami Sealed Secrets
4.1 Retrieve the Controller’s Public Certificate
Check that the Sealed Secrets controller is running:4.2 Install and Verify kubeseal
Ensure you have the kubeseal CLI:
4.3 Create the SealedSecret
Encrypt your Secret manifest:5. Configure Argo CD
Verify Argo CD is running in theargocd namespace:
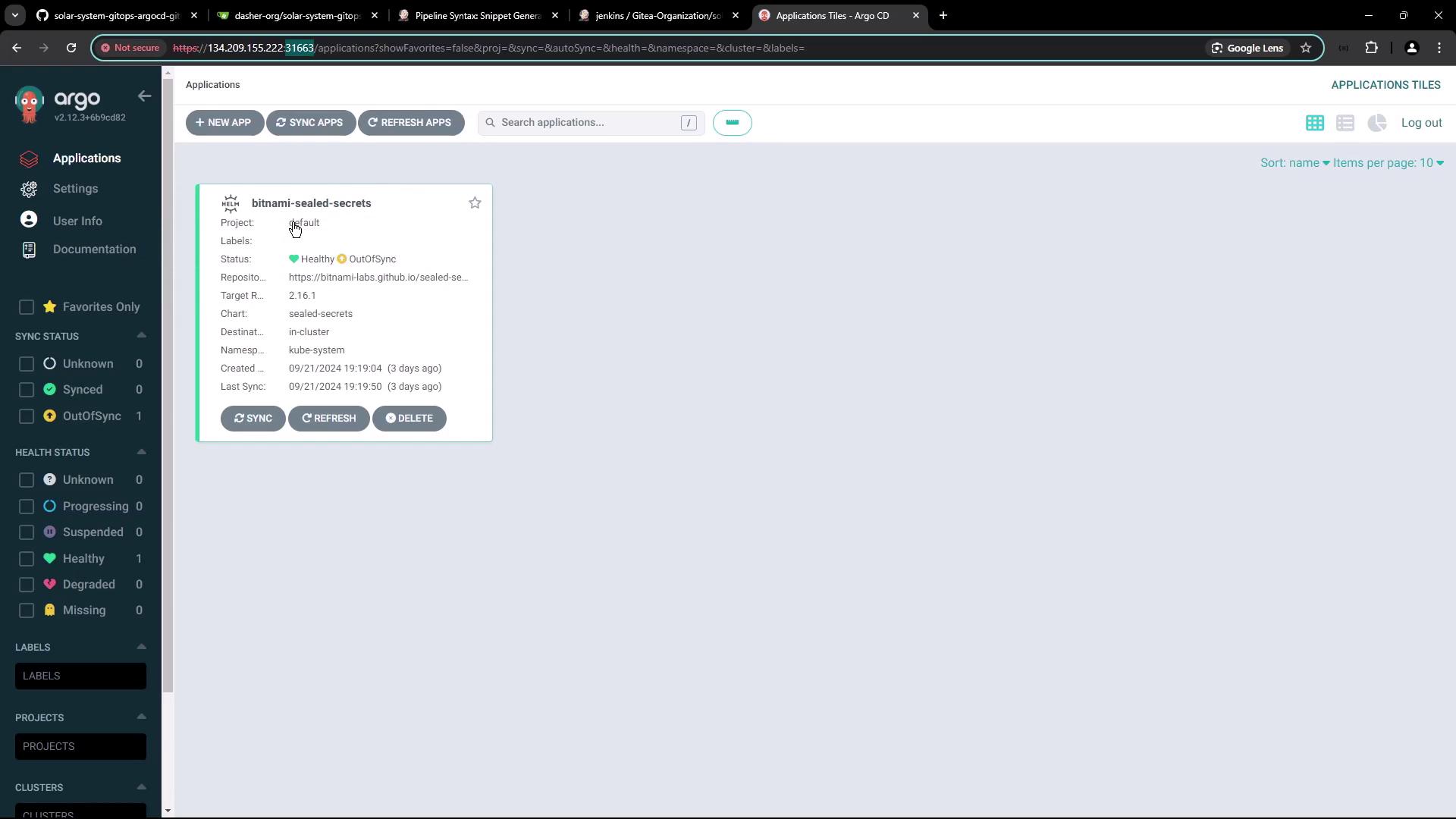
5.1 Create the Solar System Application
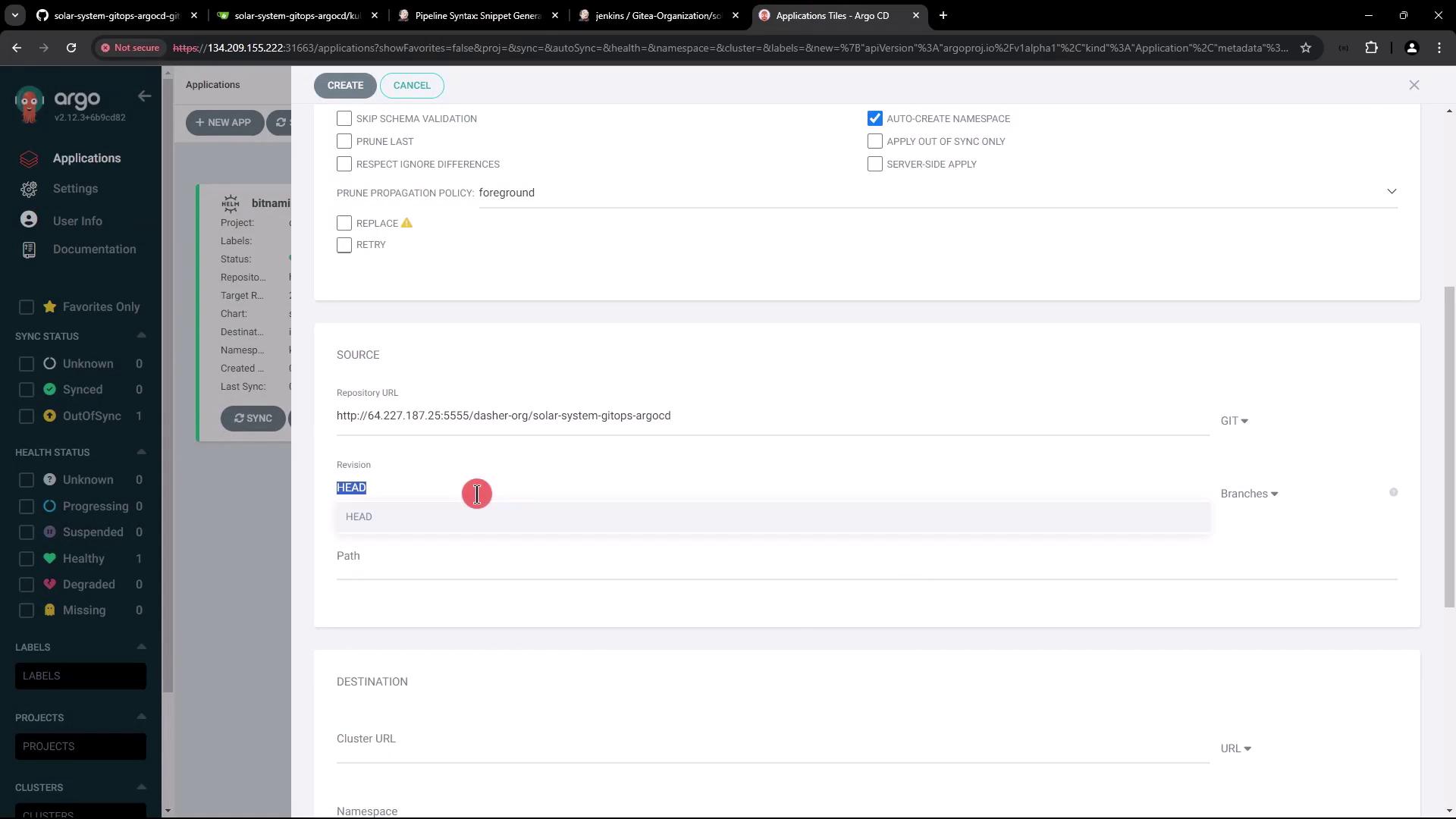
- In the Argo CD UI, click + New App.
- Enter the following:
- Application Name:
solar-system-argo-app - Project:
default - Sync Policy: Manual
- Destination Namespace:
solar-system(enable auto-create) - Repository URL:
<your-manifest-repo-url> - Revision:
main - Path:
kubernetes
- Application Name:
- Click Create.

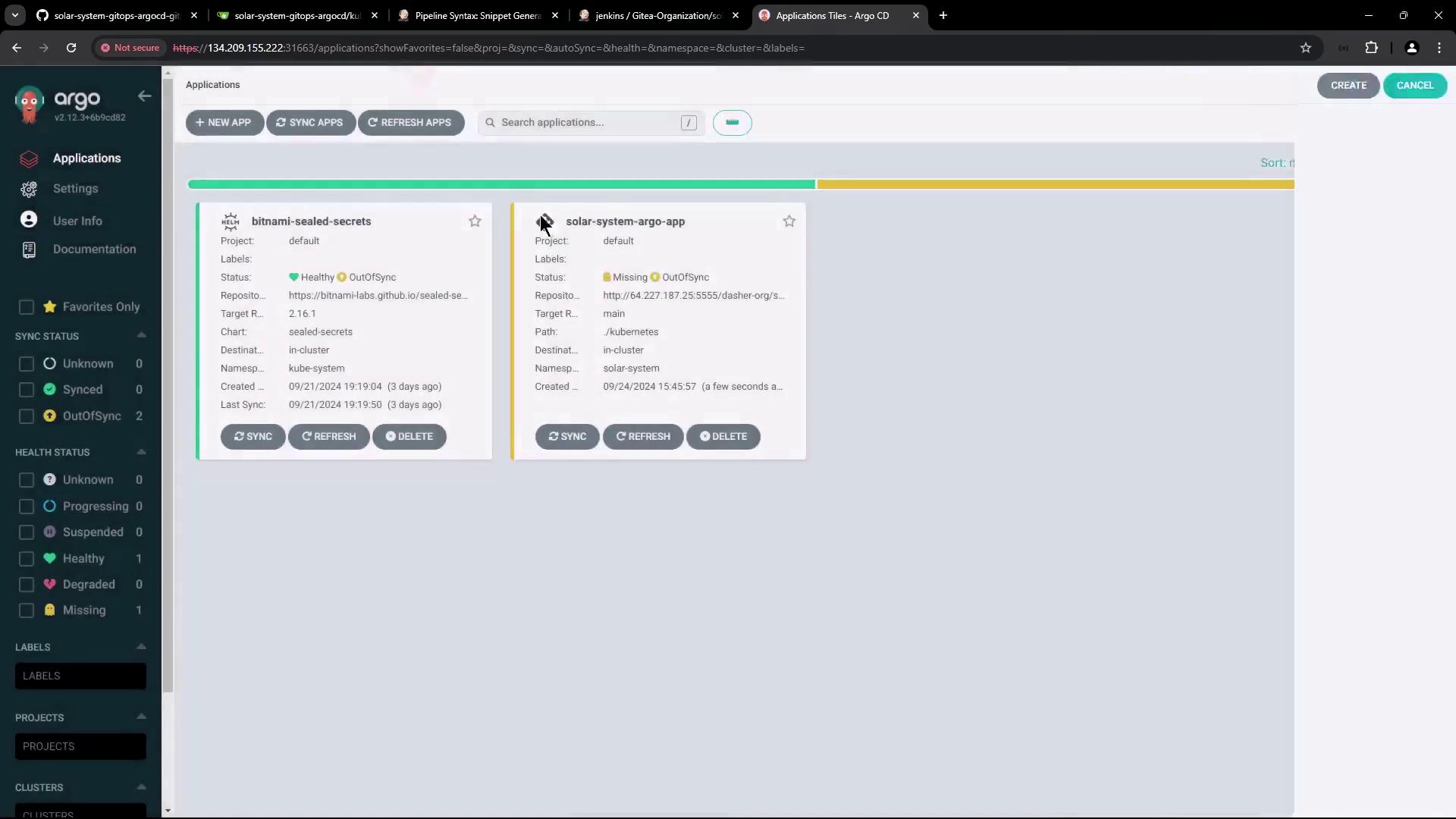
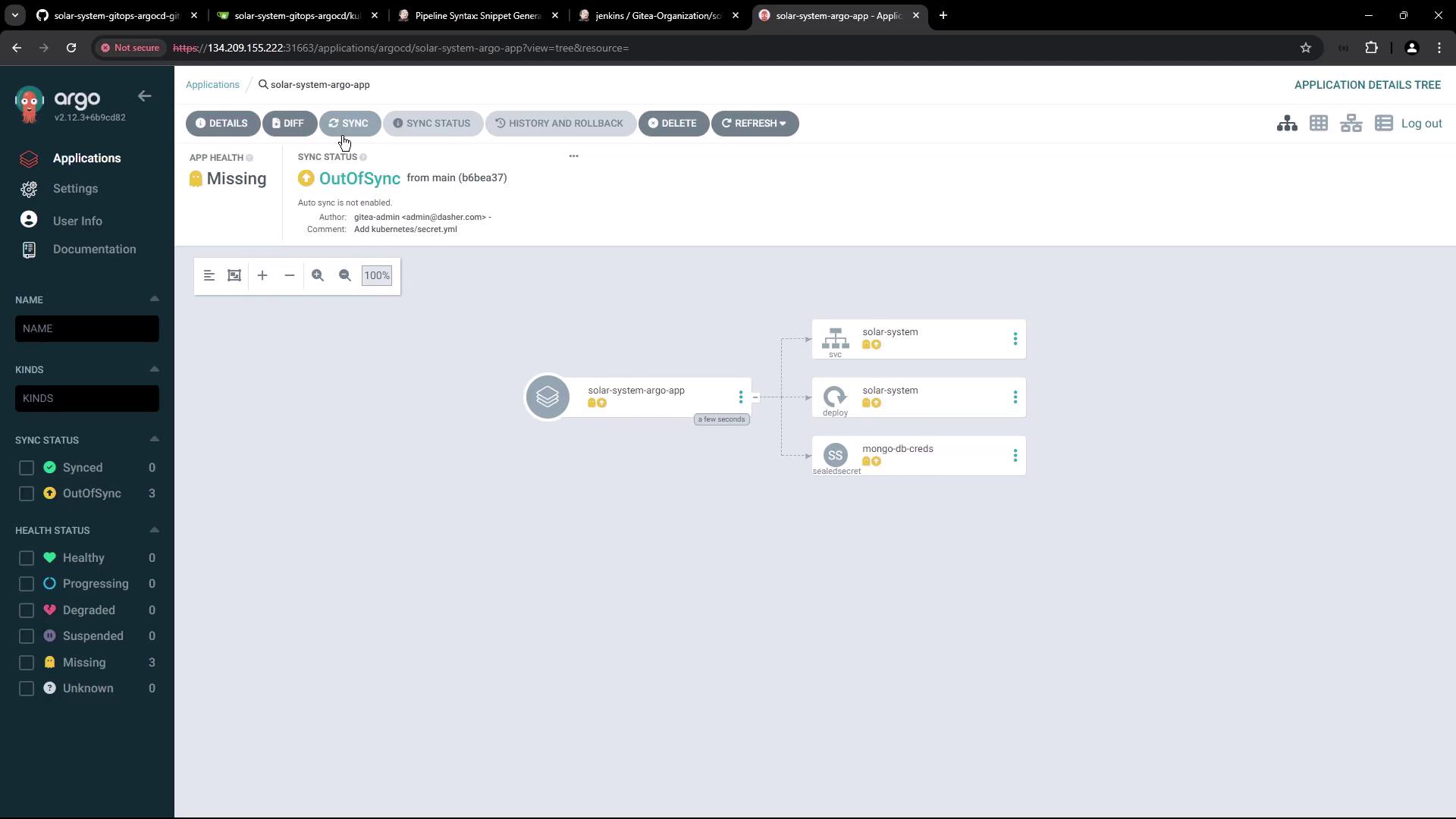
deployment.yaml (for example, bumping the Docker image tag) and push your commit, return to Argo CD and click Sync to deploy the changes.
Conclusion
You’ve now:- Cloned and migrated a Kubernetes manifest repository.
- Created and encrypted a MongoDB Secret using Bitnami Sealed Secrets.
- Configured an Argo CD application to deploy the Solar System app.