Overview
Performance design principles serve as a filtering mechanism, guiding you in deciding which concepts are essential for achieving your performance targets. When evaluating performance, consider the following questions:- What are the key performance attributes (e.g., scalability, latency, throughput)?
- Which design principles will enhance performance?
- Which principles might inadvertently affect performance negatively?
- How do you balance performance with cost and customer experience?
Principle 1: Democratizing Advanced Technologies
The first principle focuses on simplifying the implementation of advanced technologies. Instead of overburdening your IT team with the complexities of hosting or running cutting-edge technologies like NoSQL databases, media transcoding, or machine learning, you can leverage cloud services that abstract these challenges. By shifting the heavy lifting to cloud vendors, you can dynamically adjust scale and improve performance. This not only streamlines your operations but also enhances your ability to adapt to evolving performance requirements.Principle 2: Global Distribution
Global distribution involves deploying workloads across multiple regions to reduce latency and enhance user experience worldwide. Leveraging cloud-native, DevOps-enabled practices—such as infrastructure as code with tools like Terraform—ensures rapid deployment and consistent resiliency. Key points include:- Deploying services in multiple regions brings your applications closer to users.
- Automated, cloud-native solutions manage global distribution while ensuring load resiliency and failover.
Principle 3: Leveraging Serverless Architectures
Serverless architectures remove the need to manage underlying servers for traditional compute tasks. With serverless solutions, you can achieve automatic scaling and pay only for the exact resources you use, reducing operational overhead and boosting performance.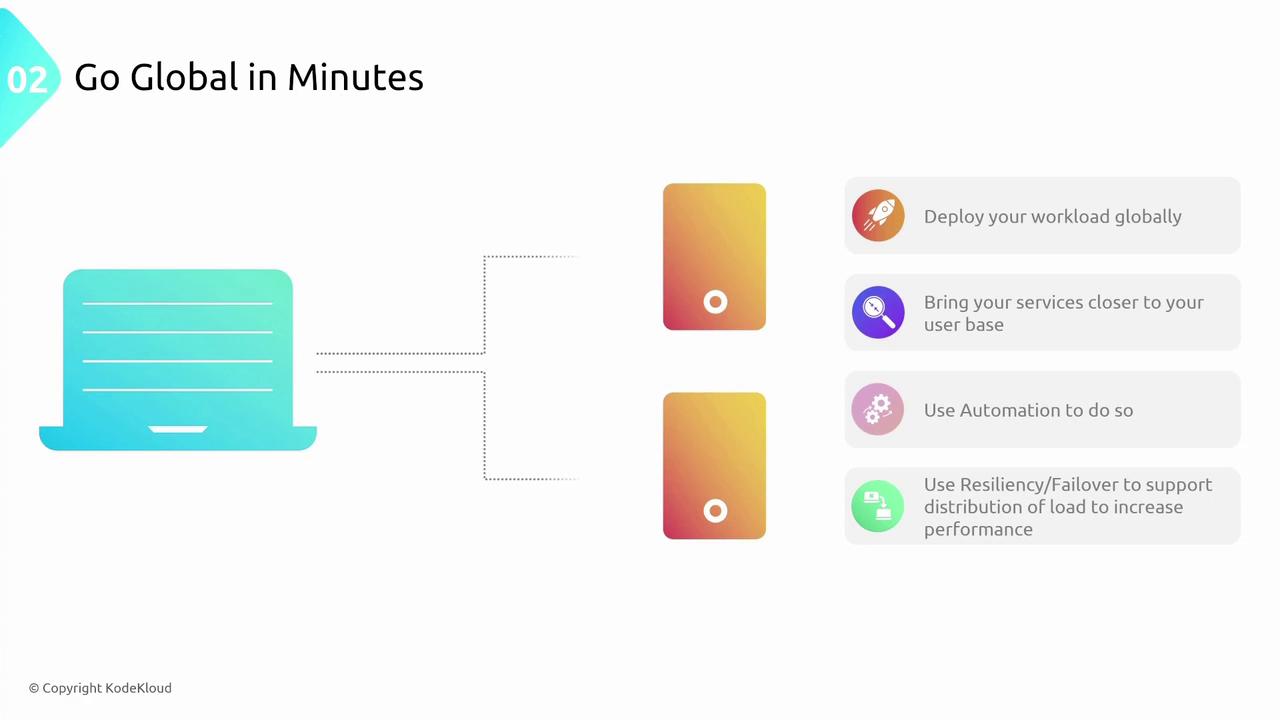
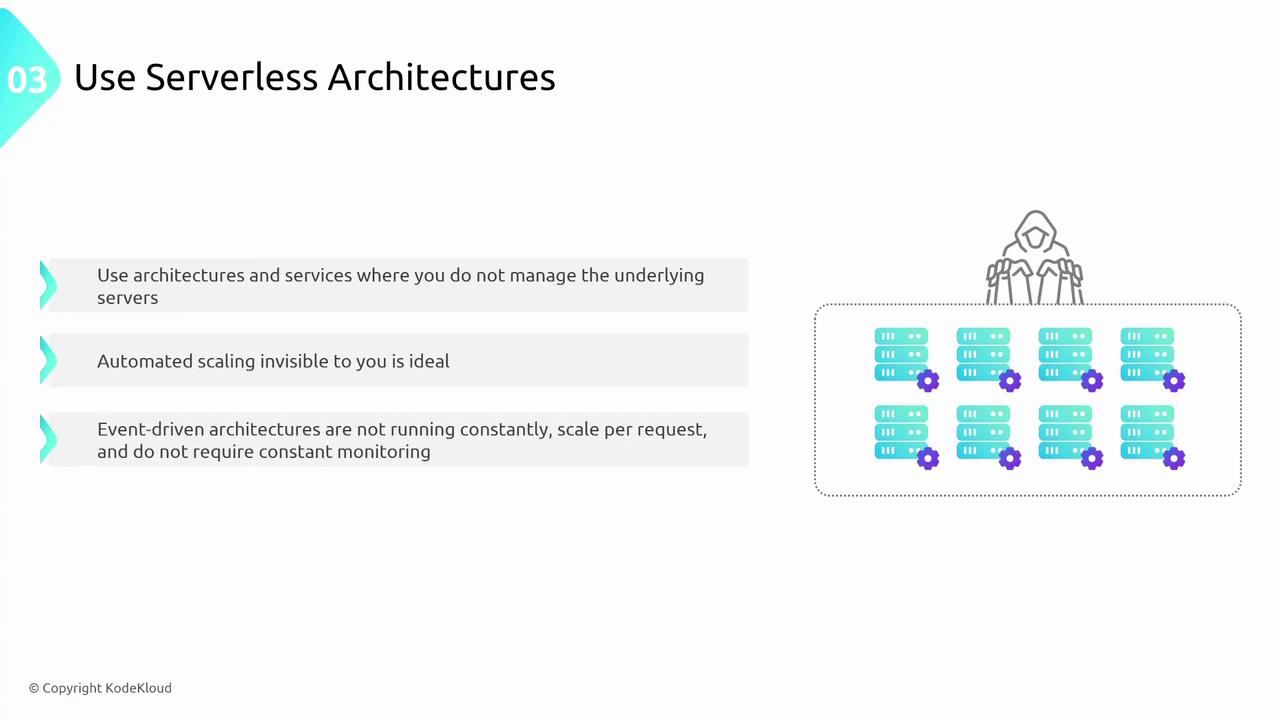
Serverless architectures trigger only when necessary, making them a cost-effective and high-performance choice.
Principle 4: Experimentation and Testing
Experimentation is essential for pinpointing the optimal performance configurations. Utilizing automated, virtual resources for comparative load testing across different instance types or storage setups can help determine the best performance-to-cost ratio. For example, testing various AWS instance sizes can reveal the configuration that offers the best value in terms of performance per dollar. Regular experimentation empowers you to innovate, optimize resource allocation, and make data-driven performance decisions.
Principle 5: Consider Mechanical Sympathy
Mechanical sympathy emphasizes using the right technology for its intended purpose, akin to selecting the proper tool for a specific task. Just as you wouldn’t use a screwdriver to drive a nail, you should avoid misusing technologies. For instance, if you need a transactional database, Amazon RDS or Aurora is preferable over DynamoDB, which is optimized for different workloads. Similarly, evaluate whether a full server is necessary for running cron jobs or if a lightweight AWS Lambda function will suffice.
Applying the Design Principles
Imagine a scenario where you require storage without the headache of managing it yourself. A serverless solution like Amazon S3 aligns perfectly with the principle of leveraging serverless technologies. If performance is a concern, consider exploring new storage classes with automated load testing to validate potential improvements. Experimentation allows you to assess various options—whether you’re evaluating S3 storage for database-like purposes or determining when to switch to Amazon RDS for better performance. Each design principle offers guidance in matching technology features with your service requirements, acknowledging that attributes like performance, security, reliability, and cost may call for different strategies.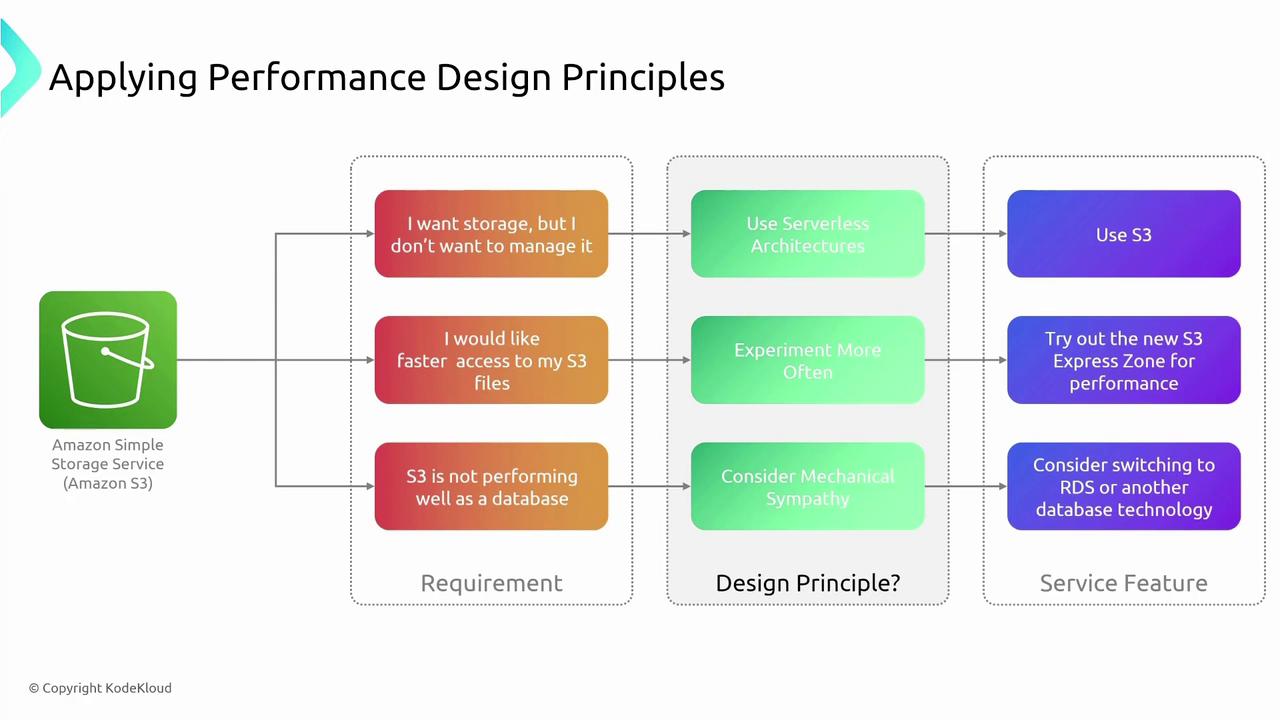
Summary
To recap, the design principles for performance include:- Democratizing advanced technologies to reduce operational complexity.
- Distributing workloads globally to lower latency and boost user experience.
- Embracing serverless architectures for automatic scaling without managing servers.
- Prioritizing regular experimentation to optimize performance and costs.
- Applying mechanical sympathy by using tools in the way they were designed.
