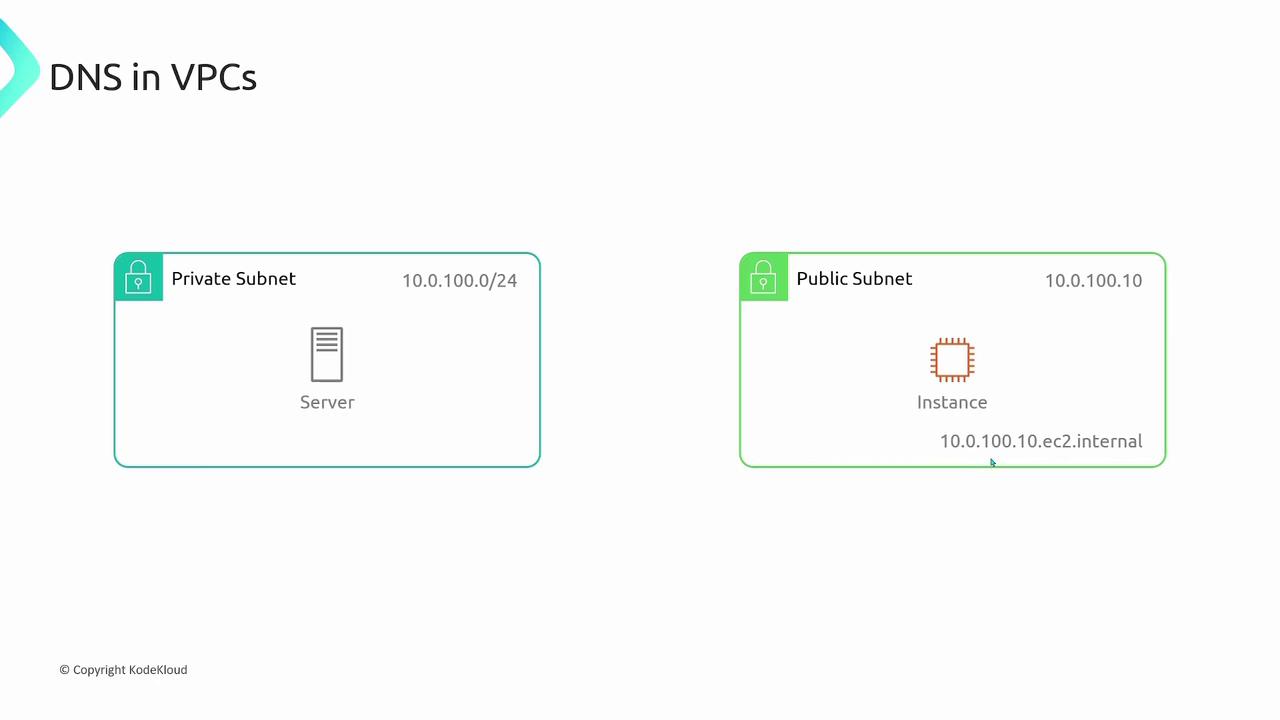
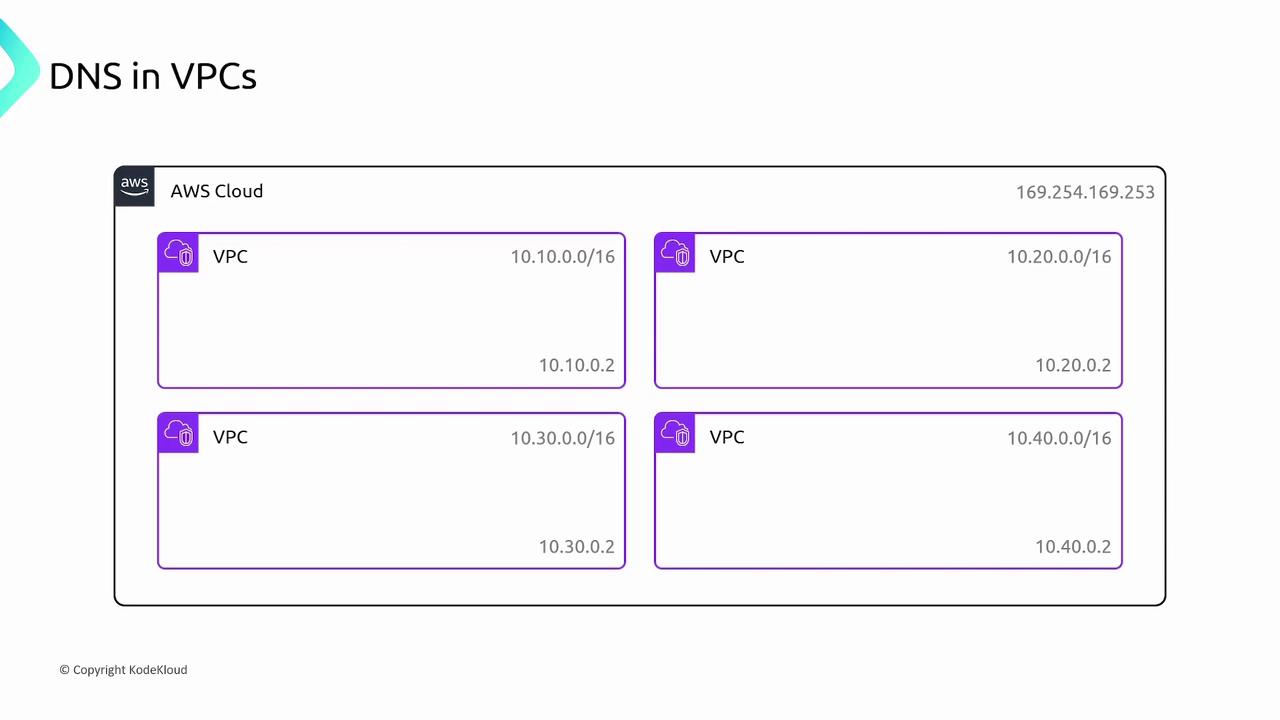
To resolve these domain names, AWS provides dedicated DNS servers. Each resource in the VPC can query these servers using one of two methods:
- Query the special IP 169.254.169.253, which is accessible by all resources in the VPC.
- Query the second IP address in your VPC CIDR block. For instance, if your VPC uses the CIDR block 10.10.0.0/16, use 10.10.0.2 as the DNS server. Similarly, for a VPC with CIDR block 10.20.0.0/16, the DNS server is located at 10.20.0.2.
-
Enable DNS Hostnames:
By default, only private IP addresses receive a DNS entry. To assign public DNS hostnames to instances with public IP addresses, ensure the “enable DNS hostnames” option is activated during VPC creation. This option is crucial for instances that need to be accessed publicly. -
Enable DNS Support:
This setting determines whether the VPC supports DNS resolution using Amazon-provided DNS servers. When enabled, DNS queries sent to the AWS DNS servers (either via the second IP in the VPC CIDR block or the special IP 169.254.169.253) will be resolved successfully. Disabling this option prevents DNS queries from reaching these servers.
- Automatic DNS Entries: Private IP addresses are automatically mapped to DNS entries.
- AWS DNS Server Access: The DNS servers can be accessed at the second IP in the VPC CIDR block or via 169.254.169.253.
- Enable DNS Hostnames: Necessary to assign public DNS hostnames to instances with public IP addresses.
- Enable DNS Support: Must be active for the VPC to resolve DNS queries using AWS-provided servers.