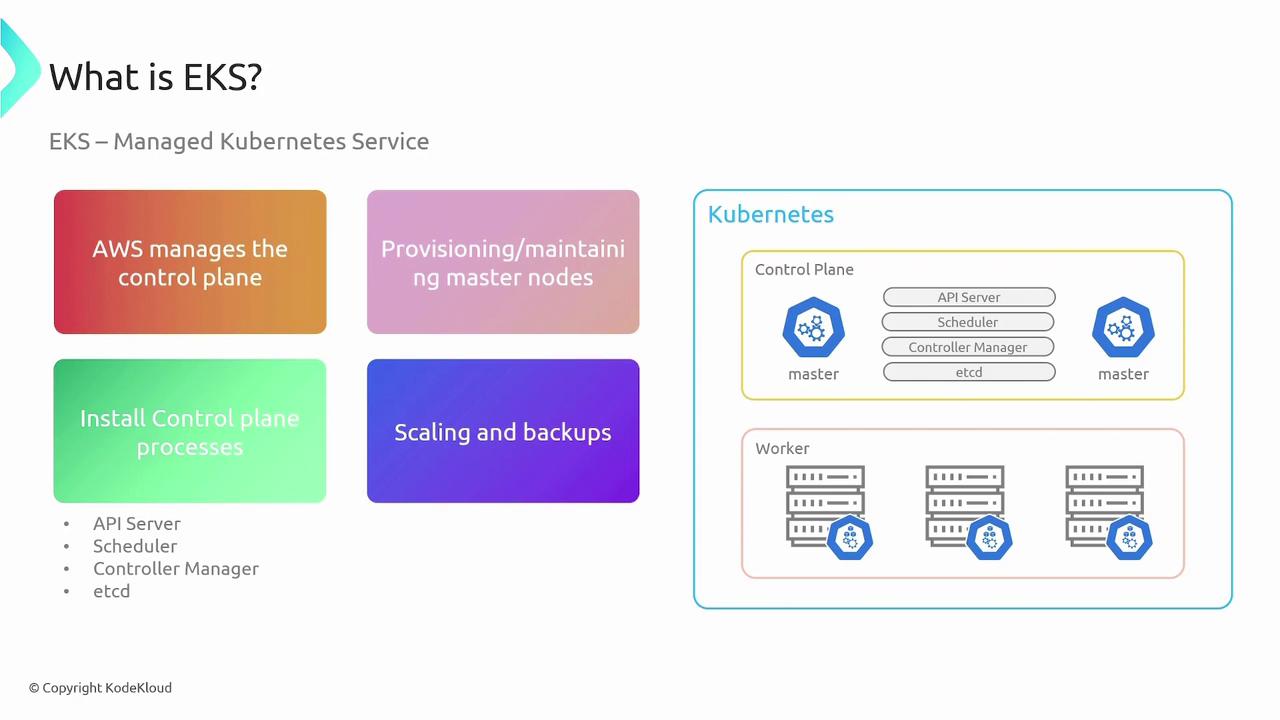
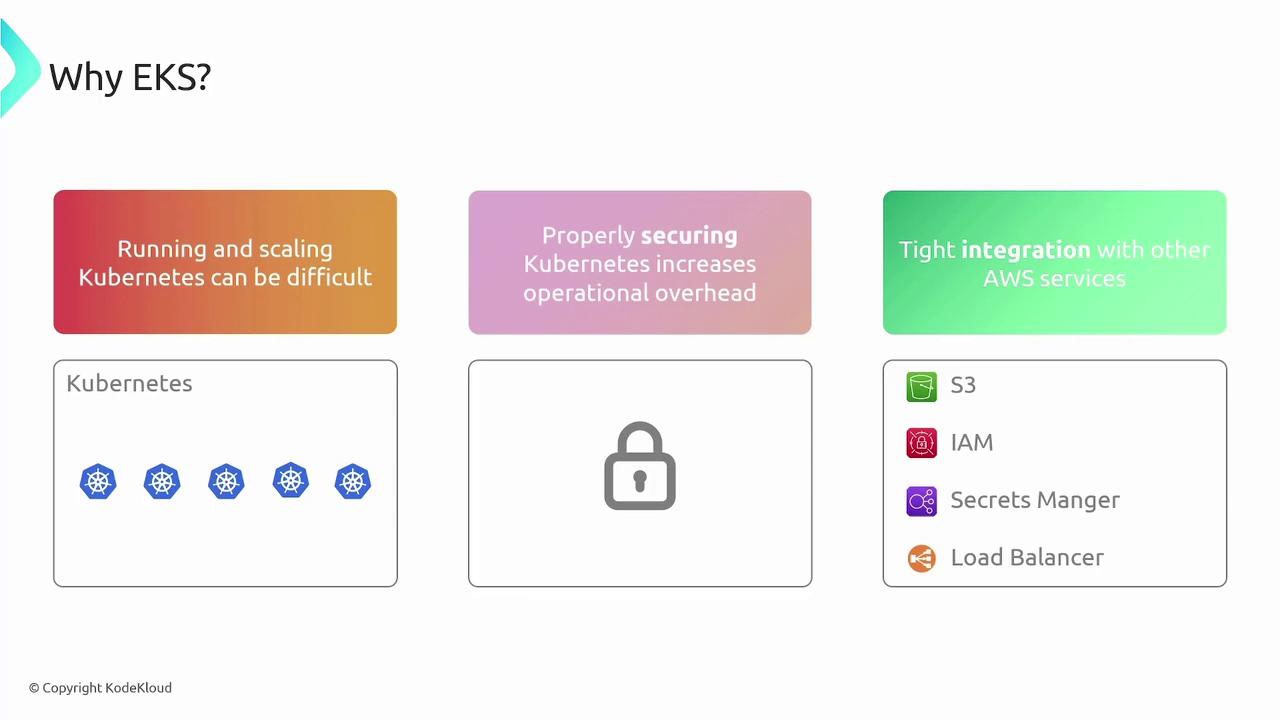
Worker Node Options in EKS
When configuring your EKS cluster, you need to decide how to manage the worker nodes. AWS provides three main options:- Self-Managed Nodes
With self-managed nodes, you manually provision EC2 instances and install all necessary components such as kubelet, kube-proxy, and the container runtime. You are responsible for handling routine updates, security patches, and ensuring that each node properly registers with the Kubernetes control plane. This approach gives you full control over your nodes, similar to managing instances in ECS.
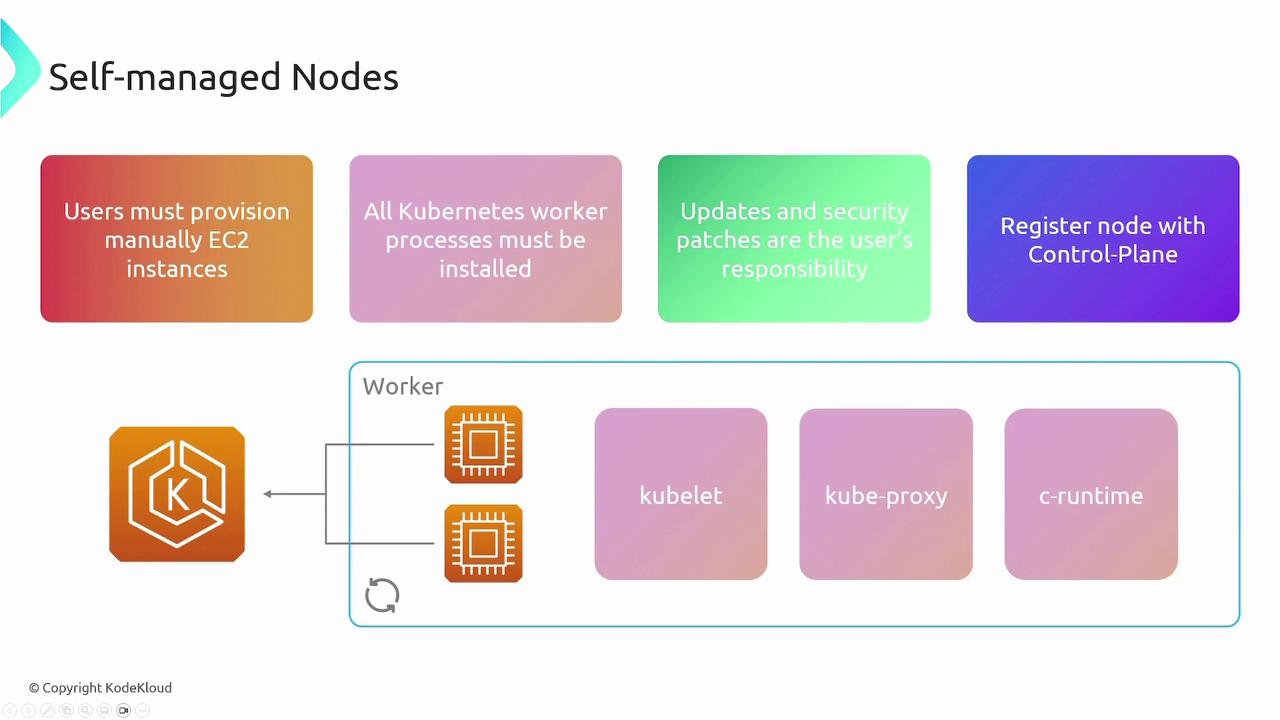
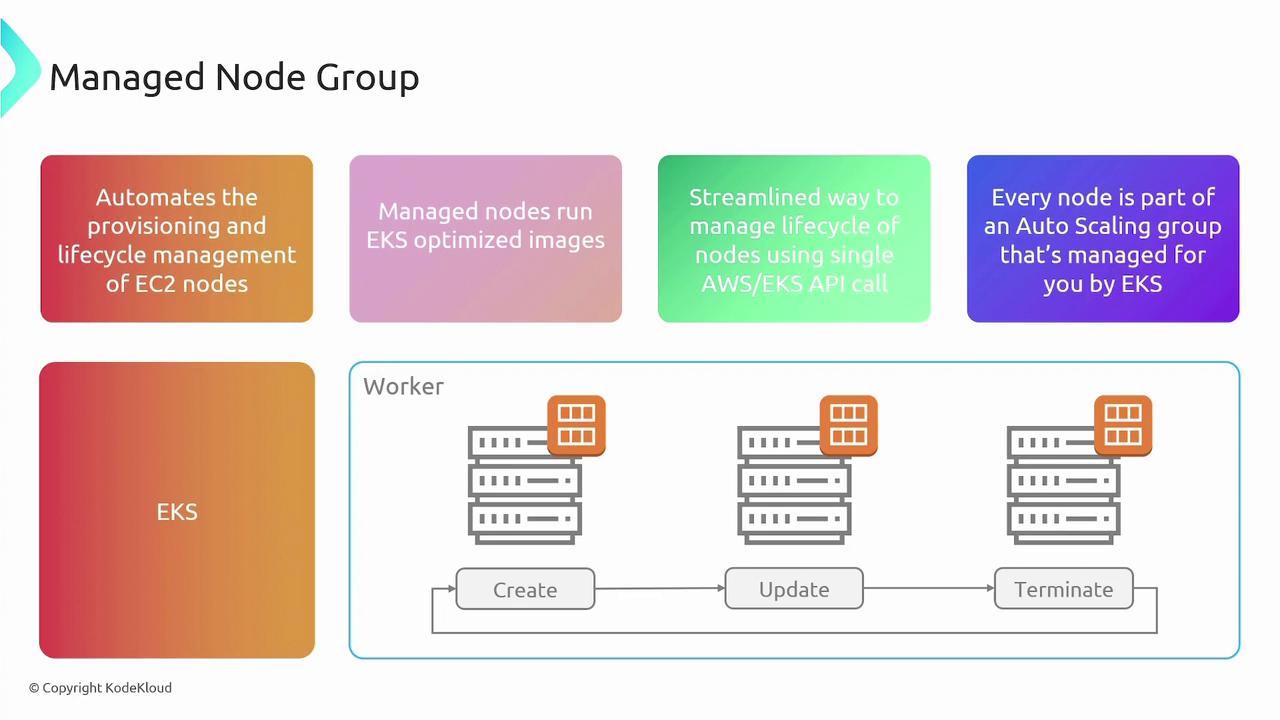
- Managed Node Groups
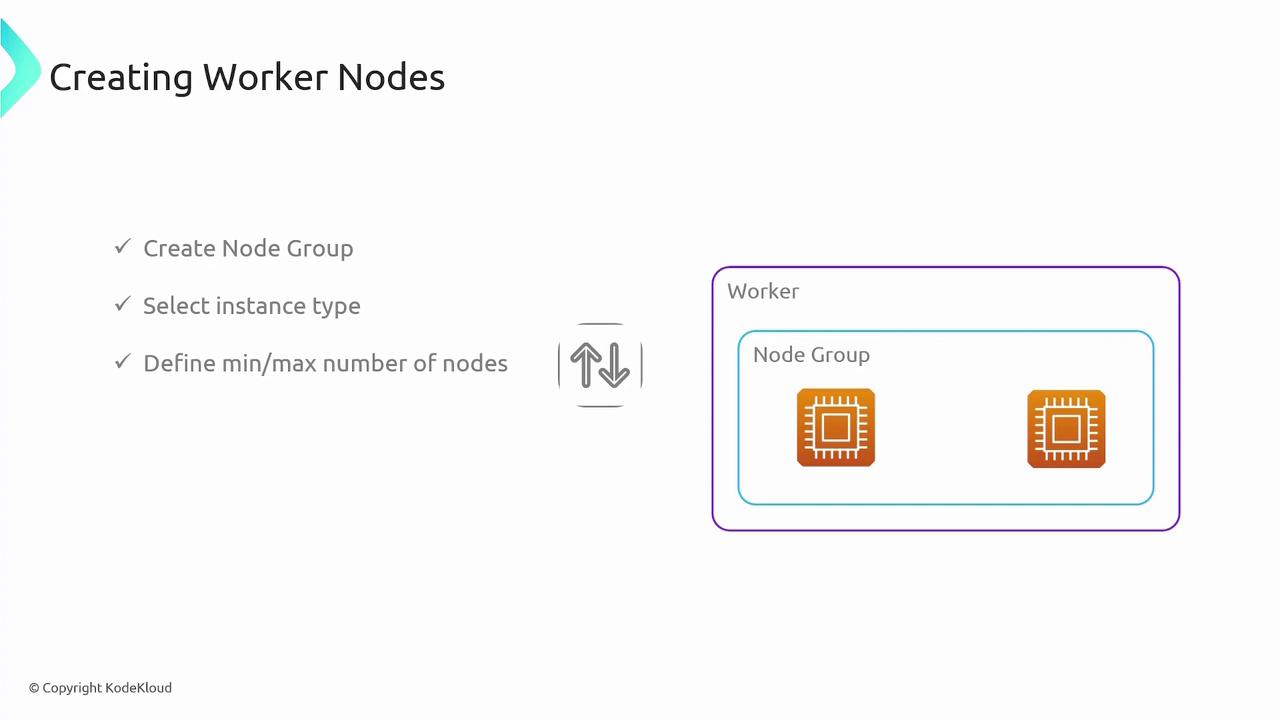
Managed node groups automate the lifecycle management of EC2 instances for worker nodes. With managed node groups, AWS deploys EKS-optimized images and simplifies operations such as node creation, updates, and termination via API calls. Nodes are configured within an auto-scaling group, reducing manual overhead while still giving you the flexibility to manage the underlying instances.
- Fargate
Fargate offers a serverless computing model for Kubernetes pods, eliminating the need to manage EC2 instances altogether. When you deploy an application, Fargate automatically provisions the necessary compute resources based on your container specifications. This model ensures you pay only for the resources you use, while AWS handles all aspects of resource management.
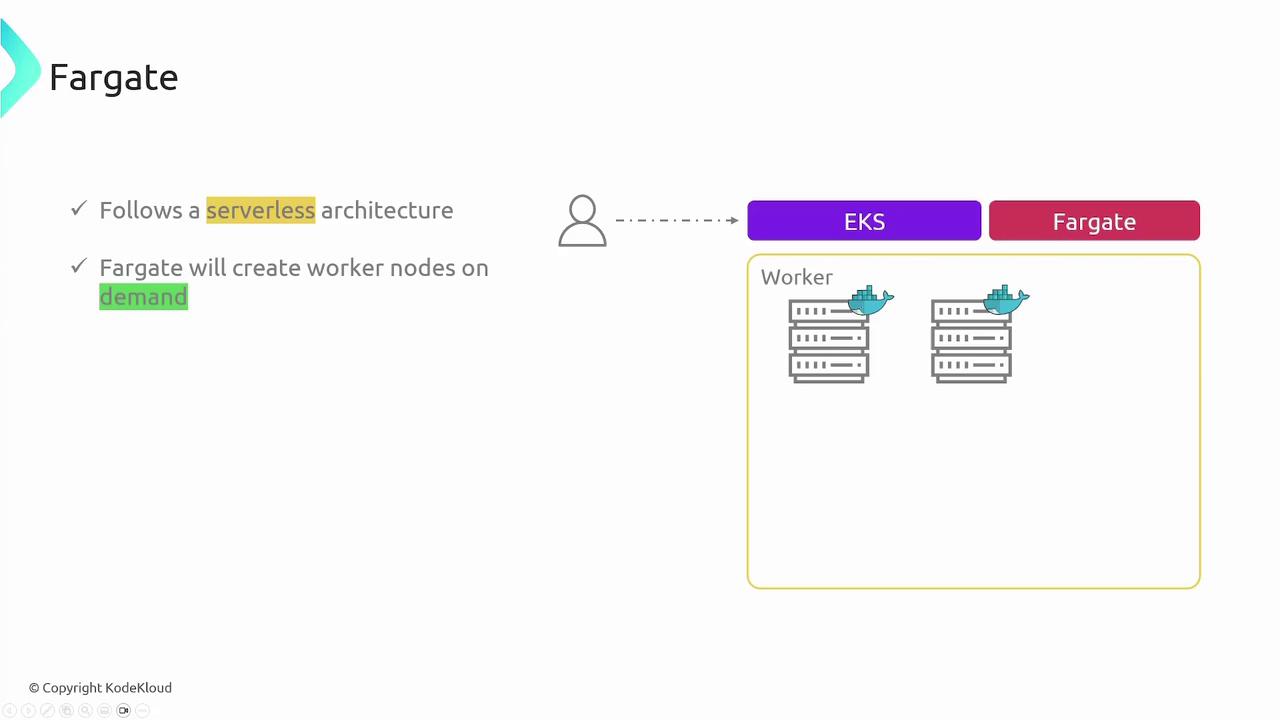
Consider your operational requirements carefully when selecting a worker node option. Self-managed nodes offer complete control, managed node groups balance automation with flexibility, and Fargate provides a hassle-free, serverless experience.
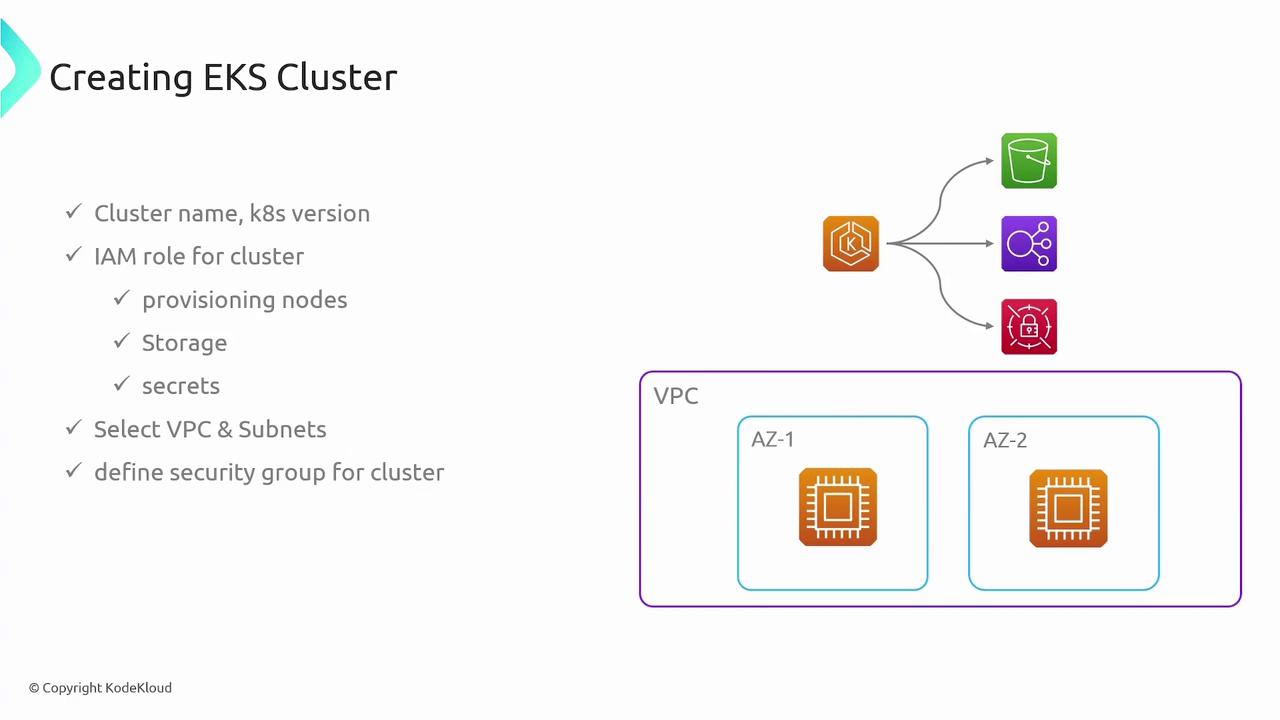
Creating an EKS Cluster
Setting up an EKS cluster involves several key steps:- Cluster Creation: Specify the desired Kubernetes version and create the cluster.
- IAM Role Configuration: Provide an IAM role necessary for cluster operations.
- Networking Setup: Define the VPC, subnets, and security groups to guarantee appropriate network and security configurations.
- Worker Node Provisioning: Choose one of the aforementioned options to deploy worker nodes.
- AWS Management Console: A user-friendly interface to create and configure your EKS cluster and worker nodes, as well as auto-configure kubectl.
-
eksctl CLI: A dedicated command-line tool that simplifies cluster creation. For instance:
- Infrastructure as Code: Use tools like Terraform or Pulumi to define and deploy your EKS cluster and associated resources programmatically.
Leveraging Infrastructure as Code not only streamlines the deployment process but also ensures consistency and version control for your EKS configurations.