Securing Amazon Redshift
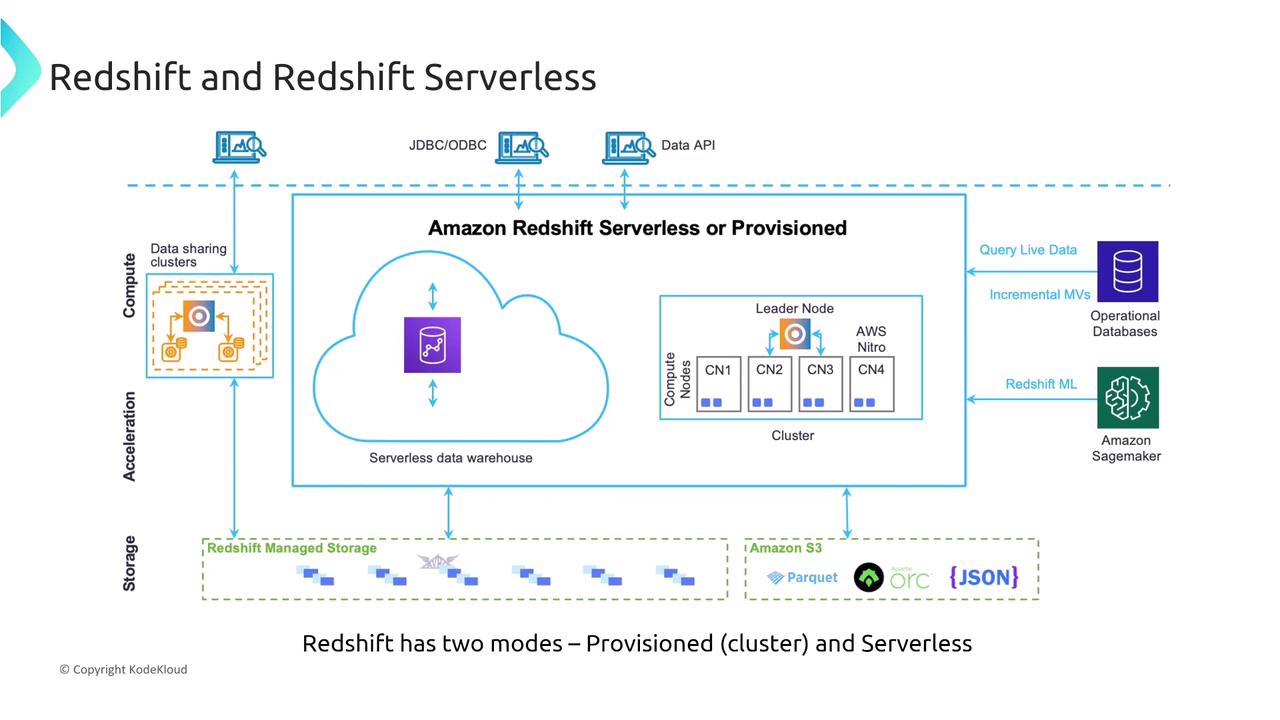
Security in Redshift is managed uniformly regardless of the deployment mode. Consider the scenario of a data analytics company deploying Redshift for big data processing. The company needs to determine which cluster configuration best describes the primary node type in Amazon Redshift.
Redshift IAM Authentication
Redshift supports IAM authentication, similar to other SQL-based databases. Over time, Redshift has evolved to incorporate several security enhancements. This process maps database users and groups to IAM users and groups. With AWS Single Sign-On (now known as the Identity Center), administrators can set up these mappings to streamline access control.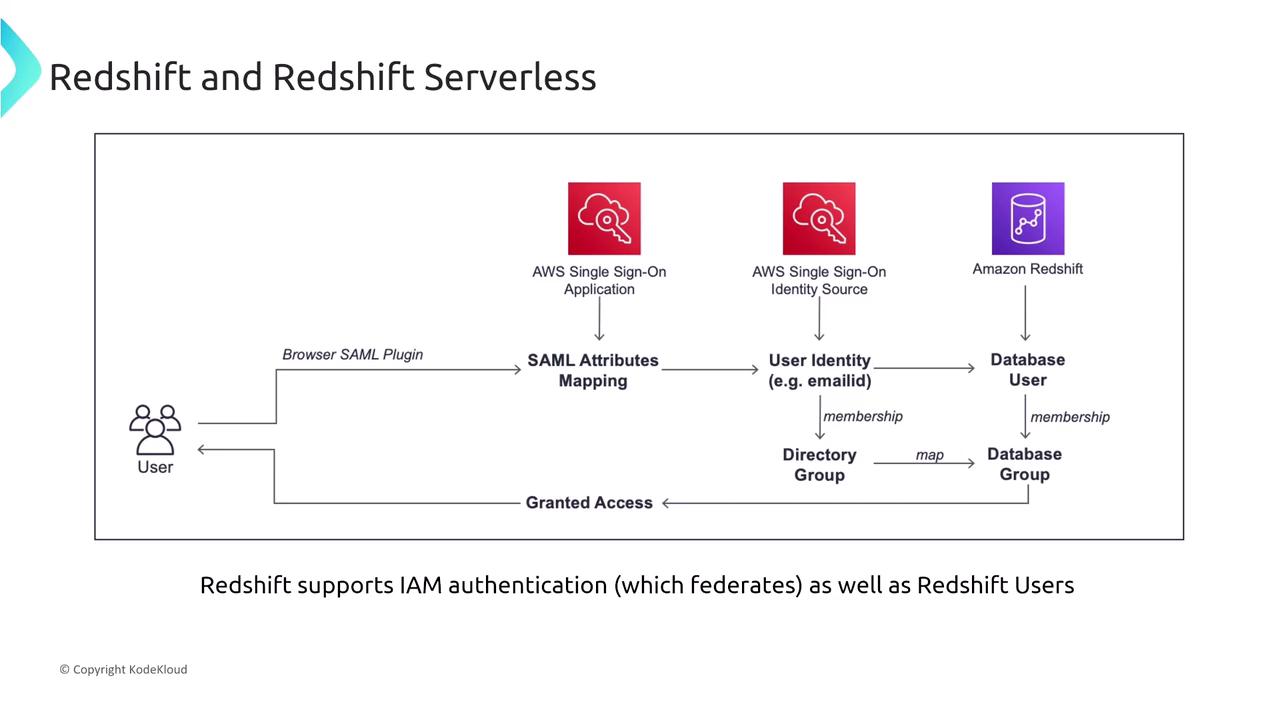
Security Groups and Network Access
Both Redshift and Redshift Serverless support the use of security groups, which function as stateful firewalls to control inbound and outbound traffic. You can configure these rules to specify which ports are accessible and from which IP addresses or VPCs, supplementing them with Network ACLs (NACLs) depending on your VPC design.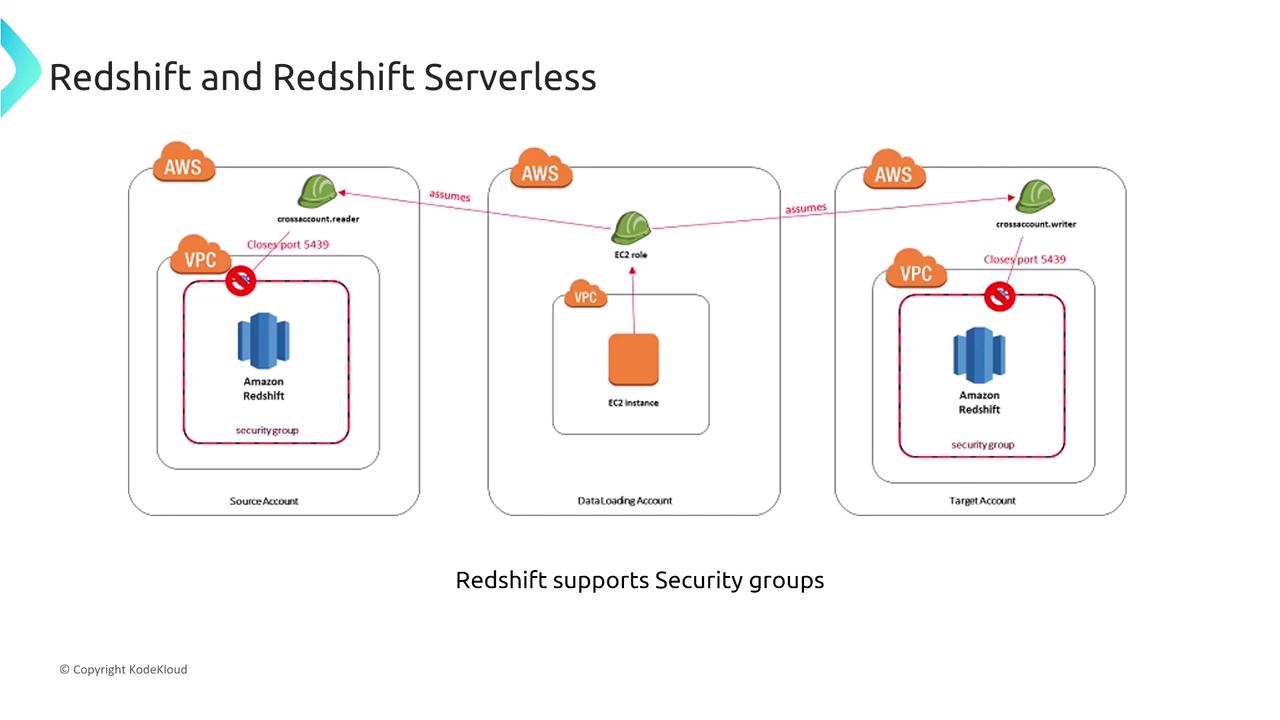

VPC Endpoints for Redshift
VPC interface endpoints powered by AWS PrivateLink are the industry standard for connecting securely to Redshift. These endpoints facilitate a private connection between your VPC and Redshift, keeping all traffic within the AWS network.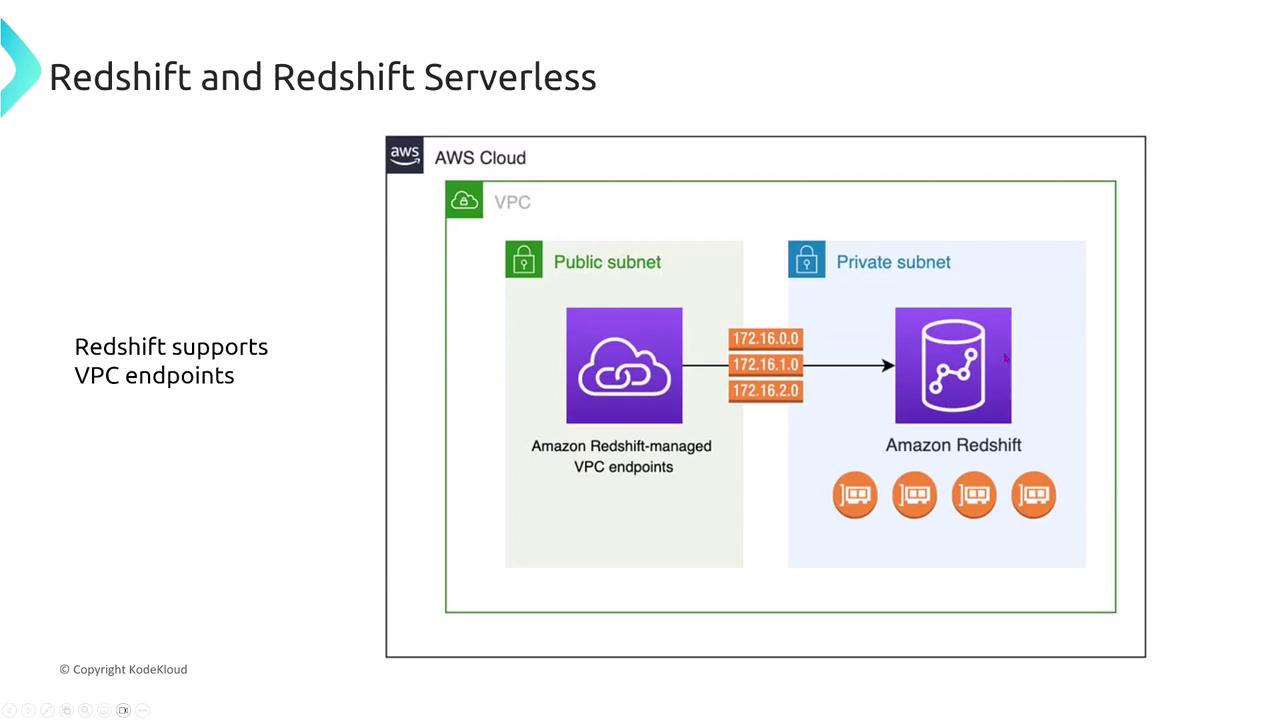
Yes, they do. The other options, which suggest performance enhancements or support for gateway endpoints, are incorrect; Redshift only supports interface endpoints.
Logging, Auditing, and Compliance
Redshift offers extensive logging capabilities. Audit logs can be exported directly to an S3 bucket, later analyzed using tools like Amazon Athena or visualized via QuickSight. Moreover, integration with CloudWatch and CloudTrail facilitates monitoring of API calls and system performance.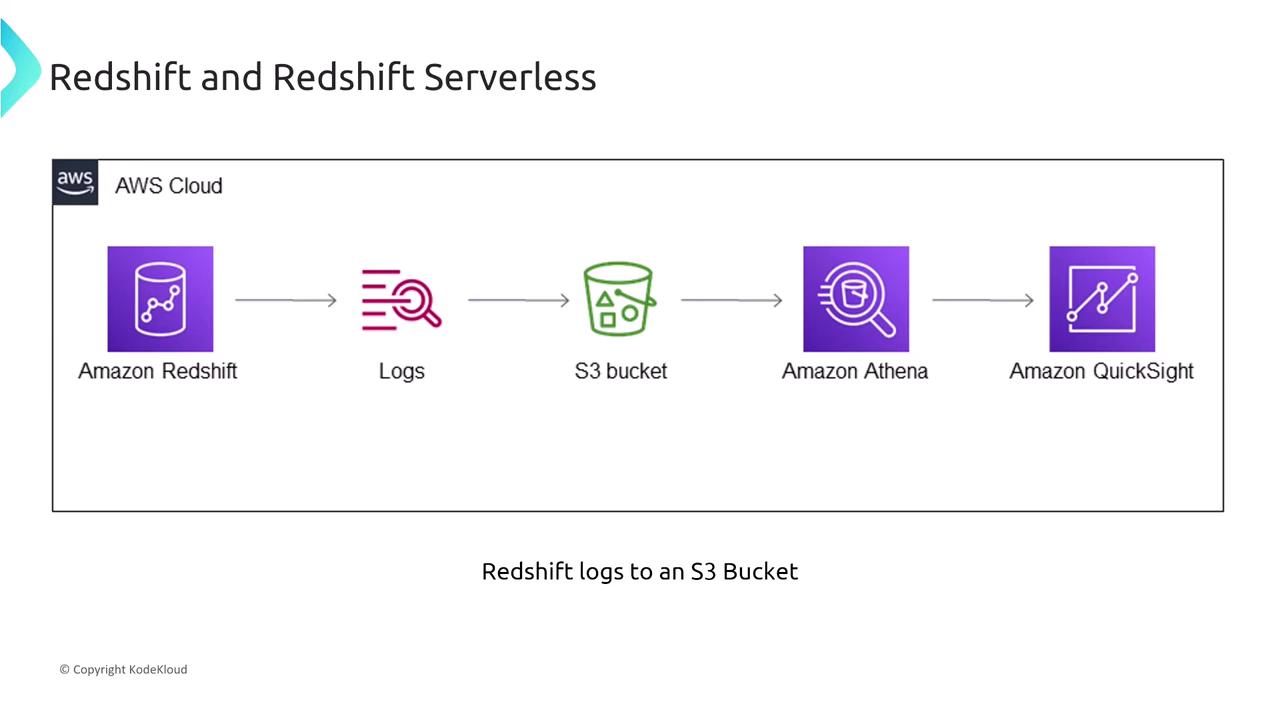


Encryption in Amazon Redshift
Amazon Redshift supports encryption for both data at rest and data in transit. You can utilize AWS Key Management Service (KMS) or an external hardware security module such as CloudHSM. Options include using AWS’s default key or a custom key from another account. Data in transit is encrypted via TLS, and integration with third-party tokenization solutions is available—note that tokenization is managed by the third-party service, not natively within Redshift.
- Enabling audit logging.
- Configuring encryption for data at rest using KMS.
- Employing TLS and tokenization (with a trusted third-party service) for data in transit.
Securing NoSQL with Amazon DynamoDB
Shifting focus to NoSQL, Amazon DynamoDB is AWS’s flagship managed NoSQL database known for its minimal operational overhead. DynamoDB automatically scales capacity based on demand, and it supports point-in-time backups without requiring manual patching or third-party tools for backup and restore. For access control, DynamoDB relies exclusively on IAM for table and row access. Since it does not employ traditional native database users, access is strictly managed through policies that include specific conditions to restrict actions on designated tables.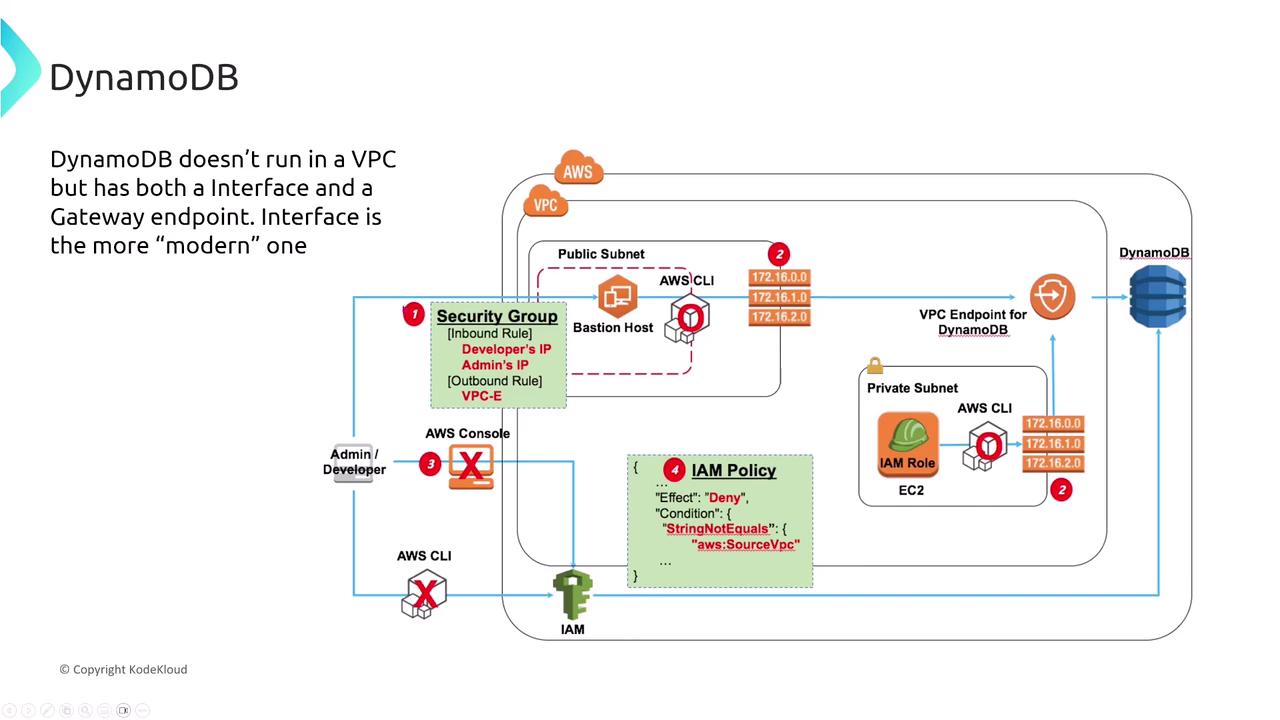
• How do you ensure that only specific IAM users or roles can access particular tables and actions?
The answer is by using IAM policies with condition keys that restrict access to designated DynamoDB tables.
VPC Endpoints and Access for DynamoDB
Although DynamoDB does not run within a VPC, it supports both gateway and interface endpoints to provide secure, private access without going over the public internet. Simply configure the appropriate VPC endpoint in your route table to set up secure connectivity.Monitoring and Change Tracking in DynamoDB
DynamoDB integrates seamlessly with CloudWatch and CloudTrail, and it also offers DynamoDB Streams—a feature enabling near real-time change data capture. This capability is particularly useful for applications such as fraud detection where immediate processing of table changes is critical.
Data Protection and Encryption in DynamoDB
DynamoDB automatically encrypts data at rest using AWS KMS and secures data in transit with TLS 1.2. This built-in encryption ensures data protection without necessitating additional configuration.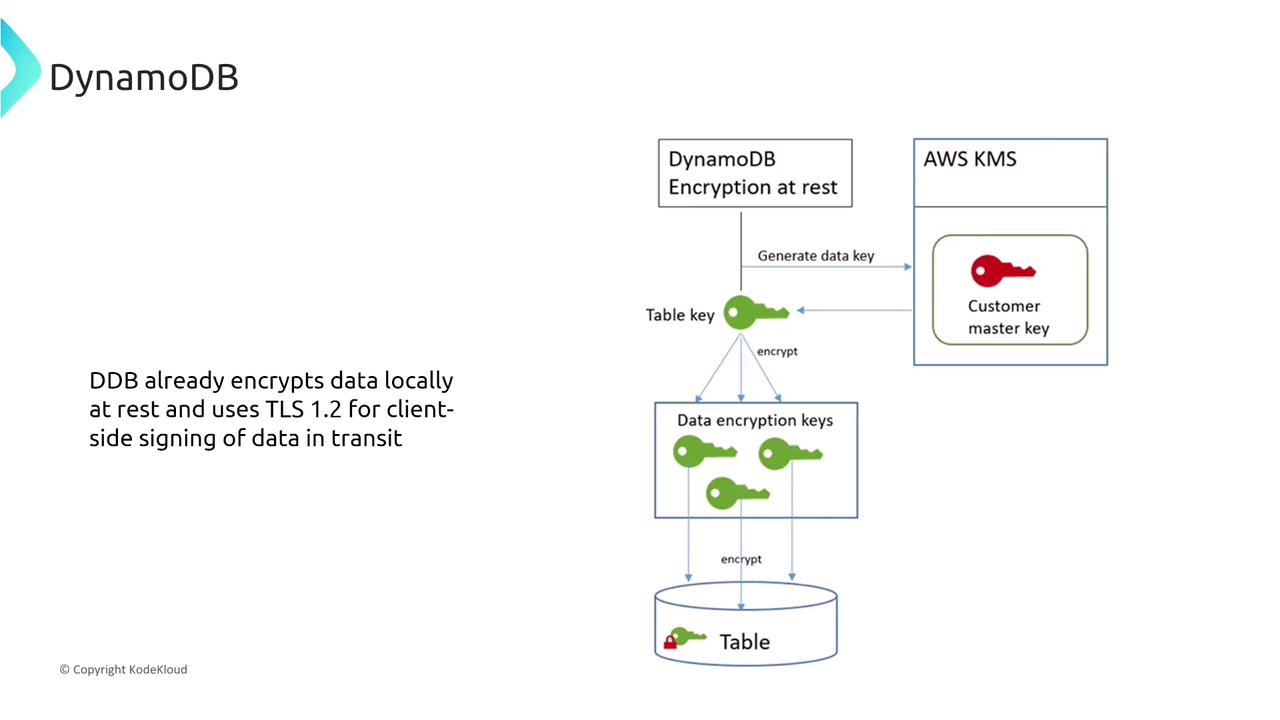
DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX)
DAX is a managed, distributed in-memory cache that boosts DynamoDB read performance by reducing latency. Despite its performance benefits, DAX has unique security requirements. Because DAX requires its own set of permissions, granting full access to DAX clusters might inadvertently widen access beyond what is intended. Always ensure that assigned IAM roles and policies for DAX are as restrictive as necessary.
Conclusion
This article has covered key security considerations for both Amazon Redshift (provisioned and serverless) and Amazon DynamoDB. For Redshift, best practices include using robust IAM authentication, setting up security groups and VPC endpoints, enabling comprehensive audit logging, and implementing encryption for data at rest and in transit. In the realm of DynamoDB, emphasis is placed on ease of management, the use of IAM for strict access control, configuring VPC endpoints for secure communication, leveraging DynamoDB Streams for near real-time data processing, and relying on built-in encryption capabilities. Additionally, DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX) offers a caching layer that boosts read performance while incorporating its own security measures.- Use IAM to manage access for Redshift and DynamoDB.
- Configure security groups and VPC endpoints to limit network exposure.
- Enable audit logging and encryption features to ensure compliance and data protection.