What Are Containers?
Containers package an application with all its necessary files, libraries, and dependencies into a portable and lightweight environment. This makes it easy to deploy your application anywhere—whether on your local machine or in production—without any additional installation steps. Think of containers as lightweight virtual machines that include only what is needed to run your application.
Challenges with Containers
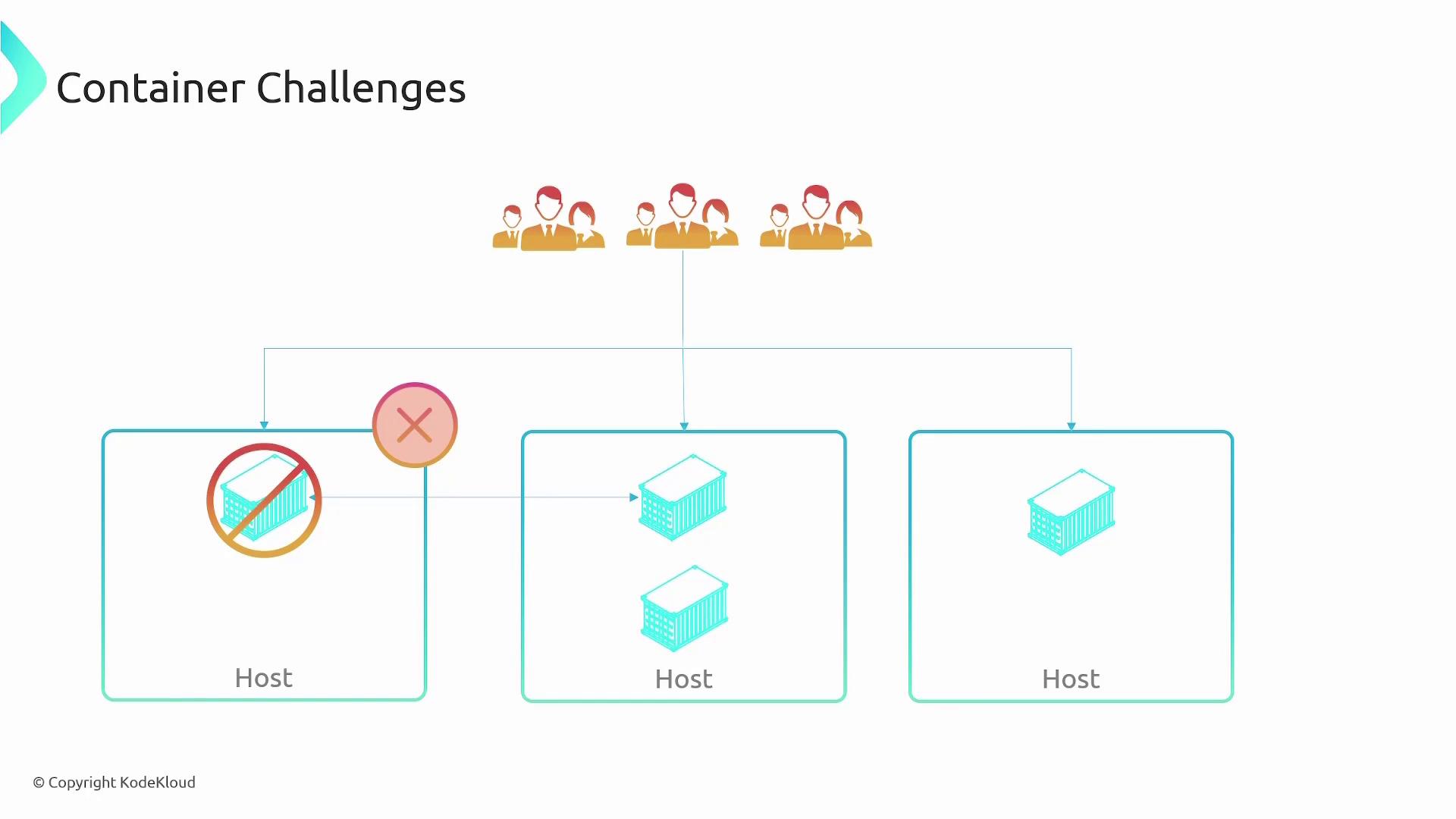
When working with containers, be aware of the following challenges:- Deploying a single container on one server creates a single point of failure. If that server goes down, your application is affected.
- For redundancy and high availability, you need to deploy multiple container instances across multiple hosts.
- Load balancing is essential to ensure even distribution of incoming requests.
- Containers often need to communicate across different networks or subnets.
- Automated monitoring is crucial to automatically redeploy containers if one fails.
- Scaling out as traffic increases (and scaling in when it decreases) is necessary for efficient resource usage.
Container Orchestrators
Container orchestrators provide a management layer for containerized environments. They handle tasks such as:- Deploying containers across multiple servers
- Load balancing requests
- Facilitating container-to-container communication
- Restarting failed containers automatically
- Relocating containers when hosts fail

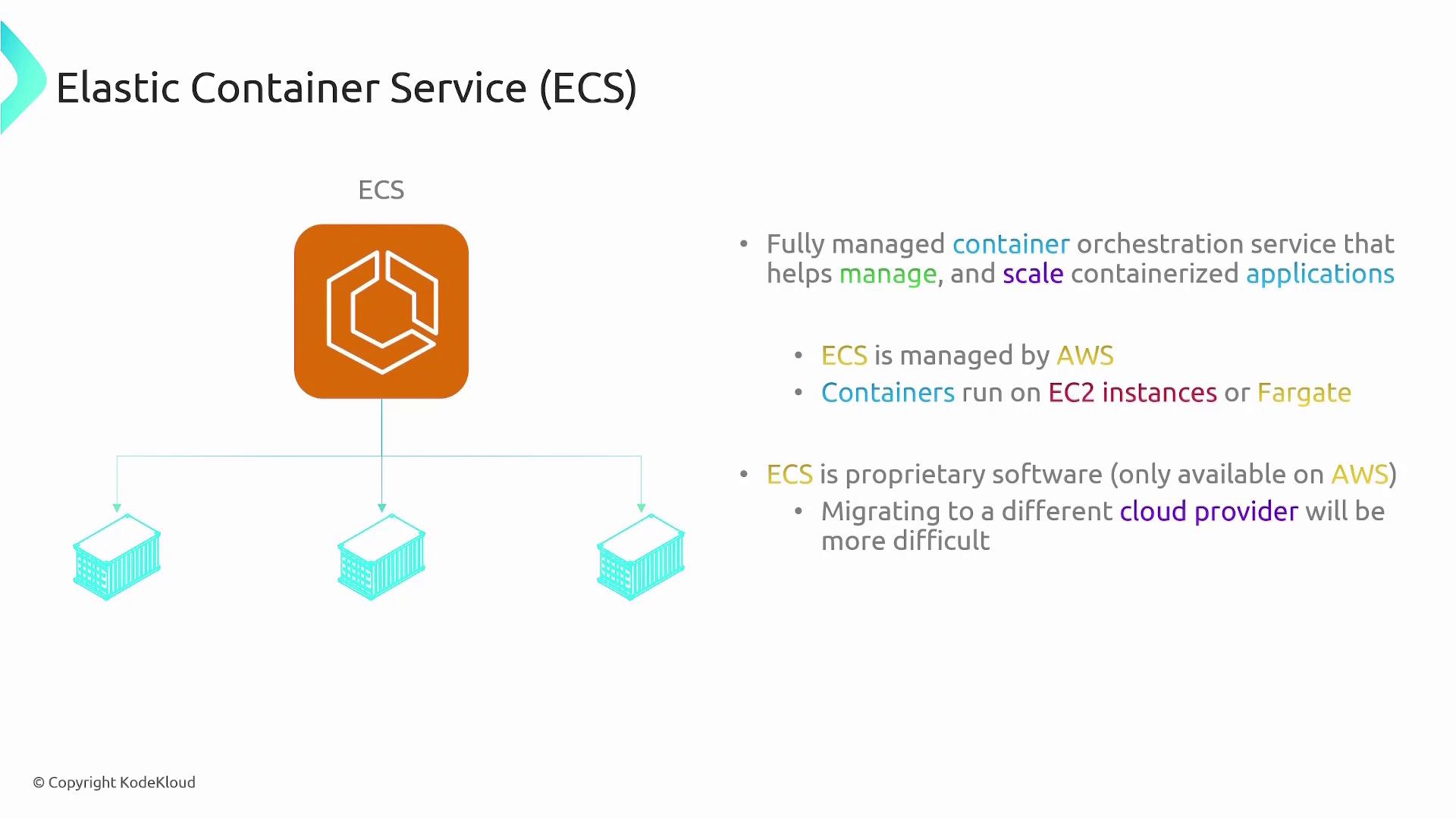
Introducing Elastic Container Service (ECS)
ECS is a fully managed container orchestration service designed to help you manage and scale containerized applications. With ECS, AWS manages the control plane—the “brains” of the operation—while you provide the compute resources. There are two primary launch options with ECS:- EC2 Launch Type: You manage your own EC2 instances as a cluster, giving you complete control over the underlying servers.
- Fargate Launch Type: AWS handles the compute infrastructure using a serverless model. You only need to specify the required configurations, and AWS provisions the compute resources automatically.
Choosing Between EC2 and Fargate
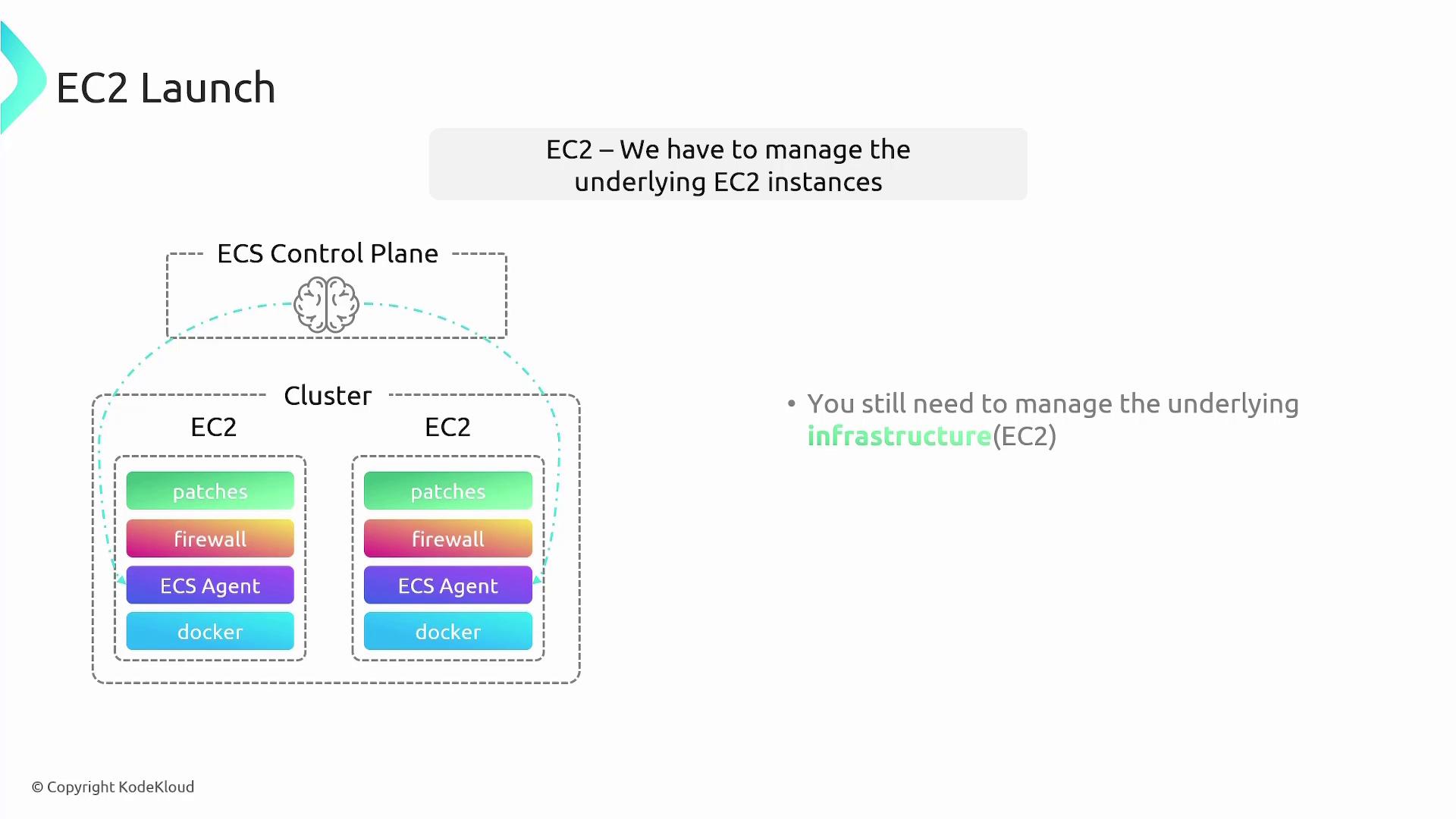
EC2 Launch Type
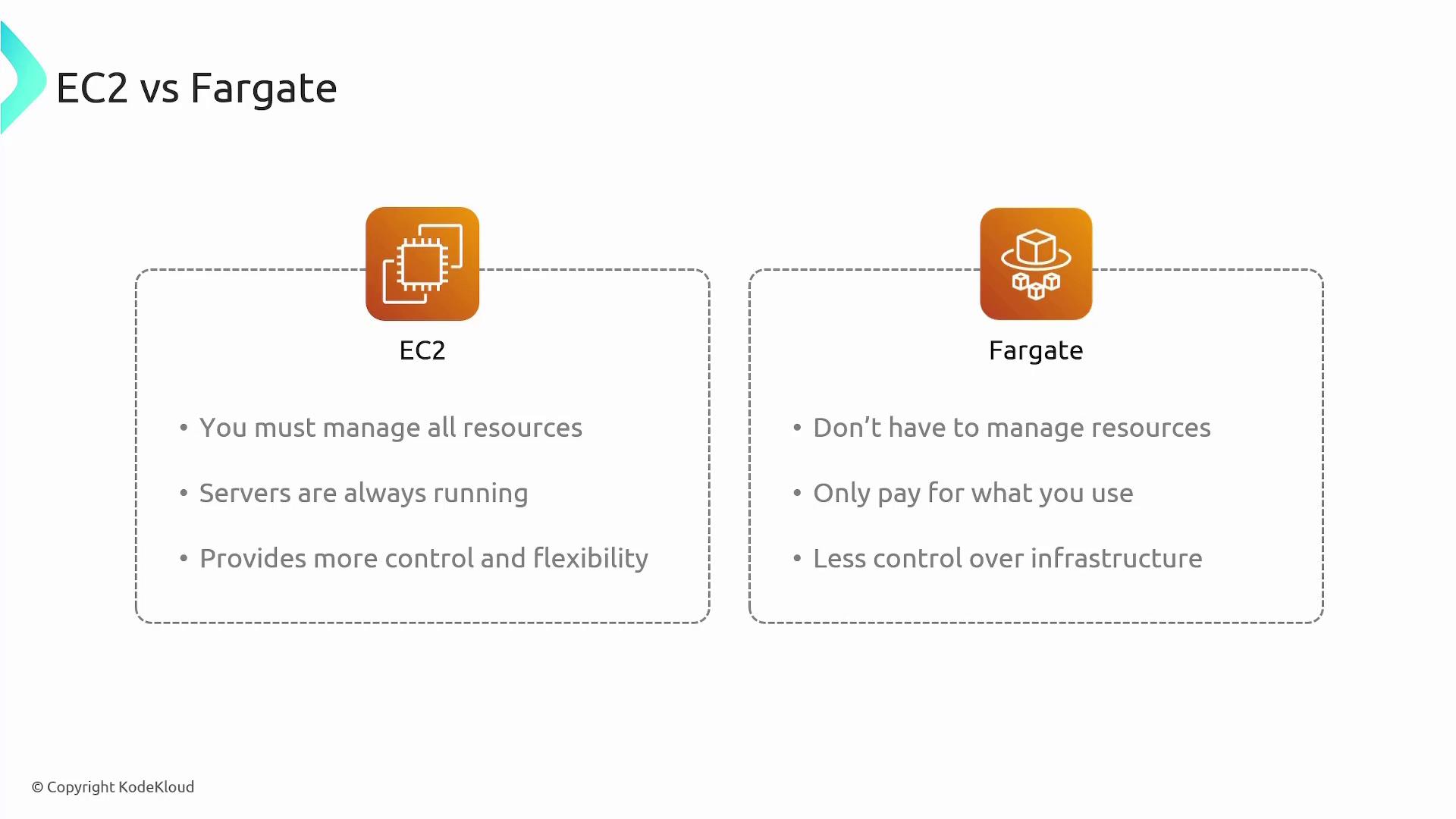
The EC2 Launch Type requires you to manage the underlying EC2 instances. This includes tasks like:- Provisioning and configuring EC2 instances
- Installing Docker and the ECS agent for communication with ECS
- Managing firewall and overall security configurations
- Applying patches and updates to maintain secure infrastructure
Fargate Launch Type
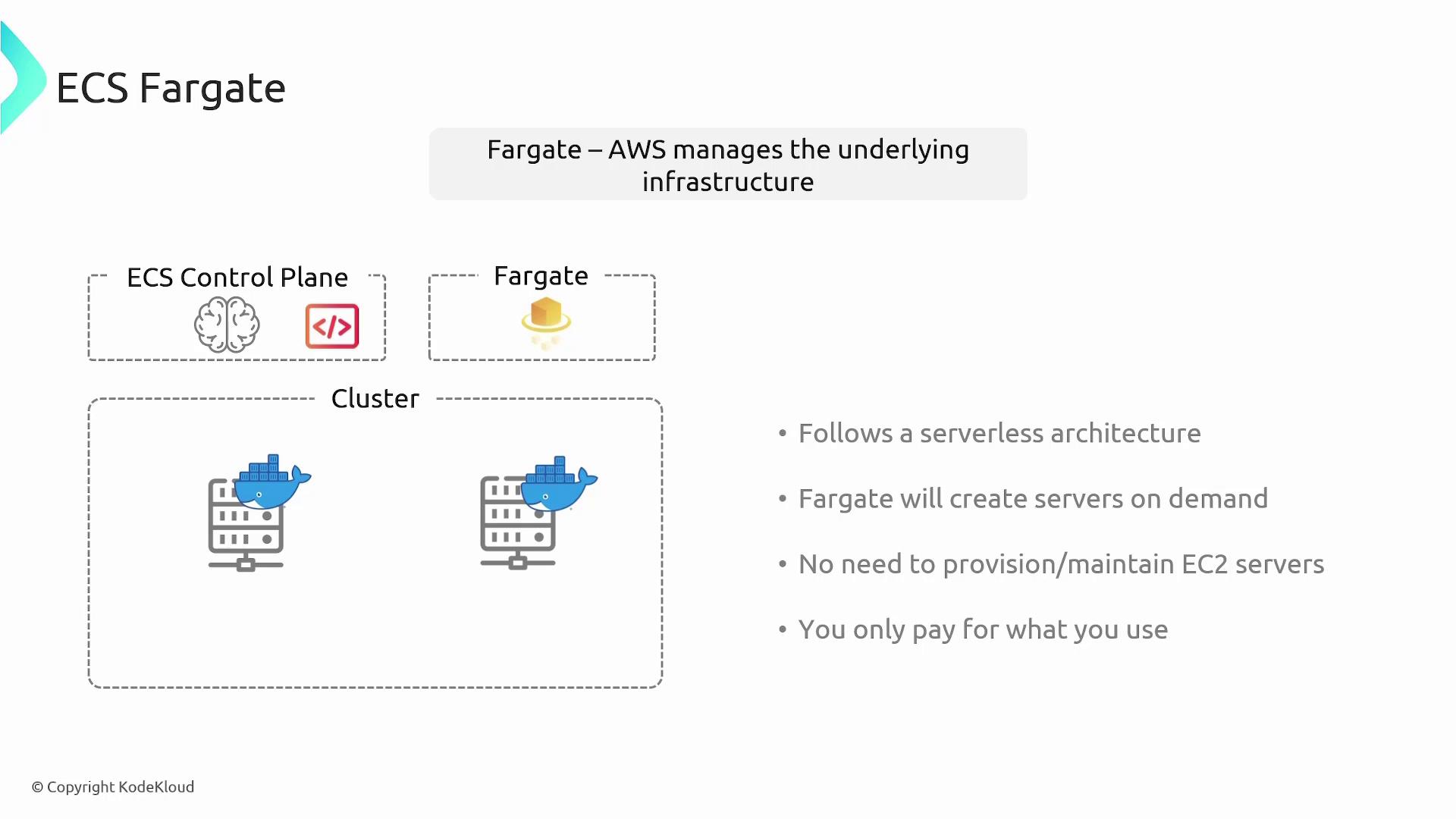
Fargate, on the other hand, offers a serverless approach where all infrastructure management is handled by AWS. You do not provision or maintain EC2 instances. Simply define your container configuration parameters (such as compute and memory requirements), and Fargate provisions the necessary compute resources on demand. This option follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model, making it cost-efficient.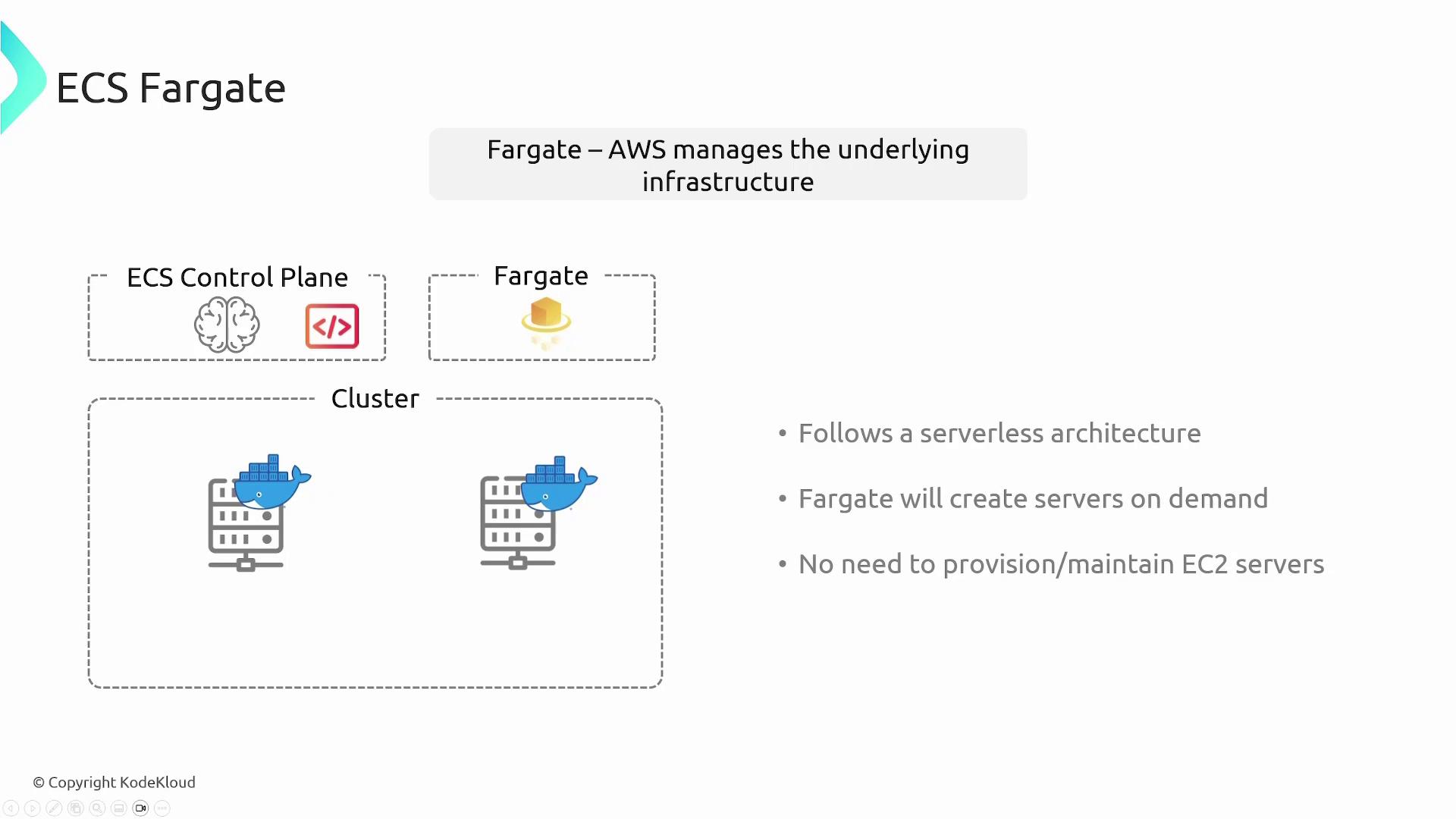
- EC2: Requires upfront resource management, runs continuously, and offers enhanced control.
- Fargate: Minimizes management overhead, operates on a pay-as-you-go model, and streamlines the deployment process.
Understanding ECS Tasks and Task Definitions
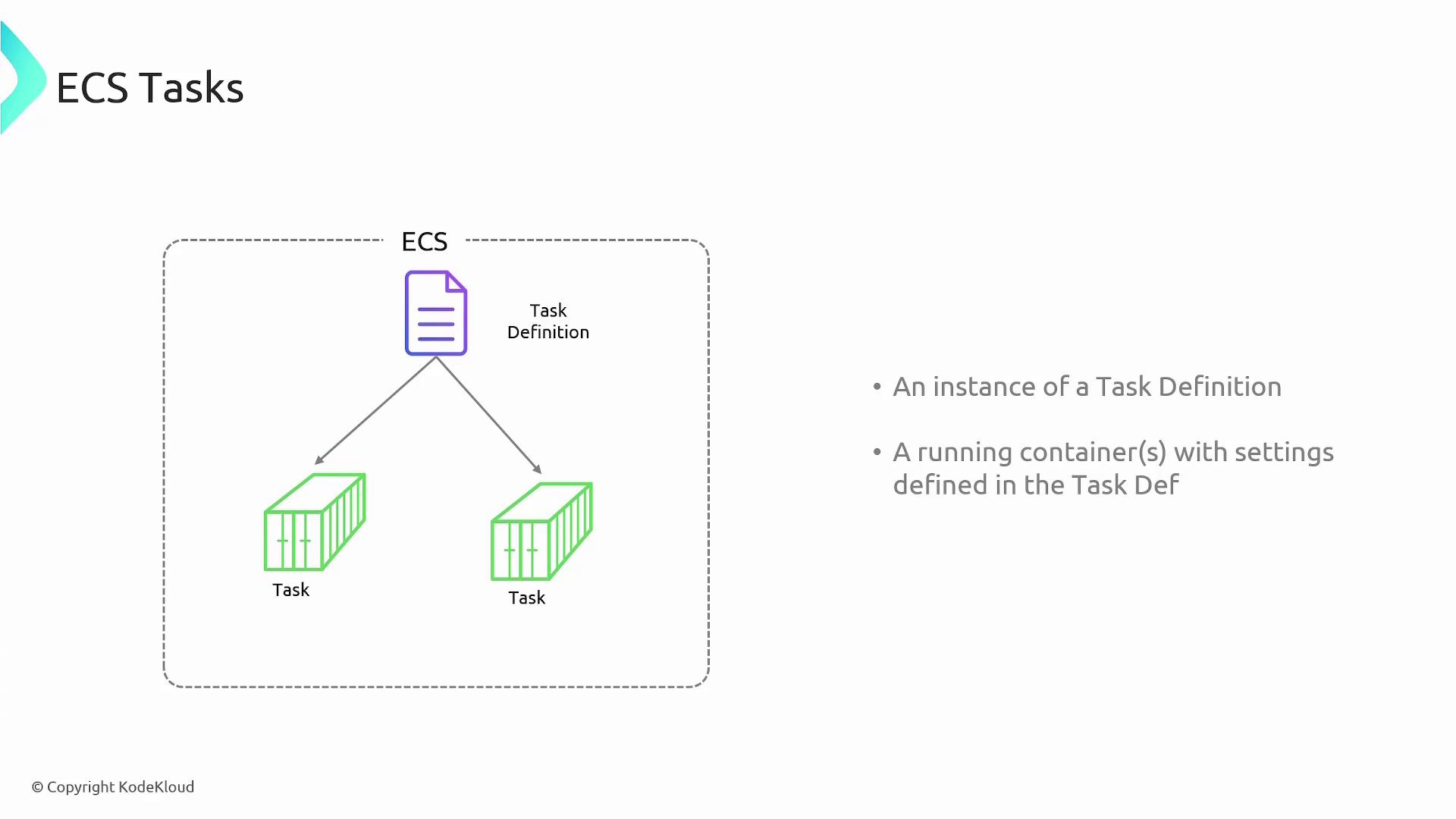
A key concept in ECS is the task, which is an instantiation of a task definition.Task Definitions
Before running containers on ECS, you first create a Dockerfile for your application, build an image, and upload it to a repository like Docker Hub. To launch this image on ECS, you define a task definition—a blueprint that includes details such as:- The container image to use
- Memory and CPU allocations
- Port mappings
- Volume configurations
- Dependencies and other container settings
ECS Services
An ECS service ensures that a specified number of tasks (containers) are always running. When you create an ECS service, you associate a task definition with the desired number of instances. For instance, if you’re deploying a Python application, you might define its task and then create a service to maintain two or more instances. If a task fails or if an instance goes down, the service will automatically redeploy it.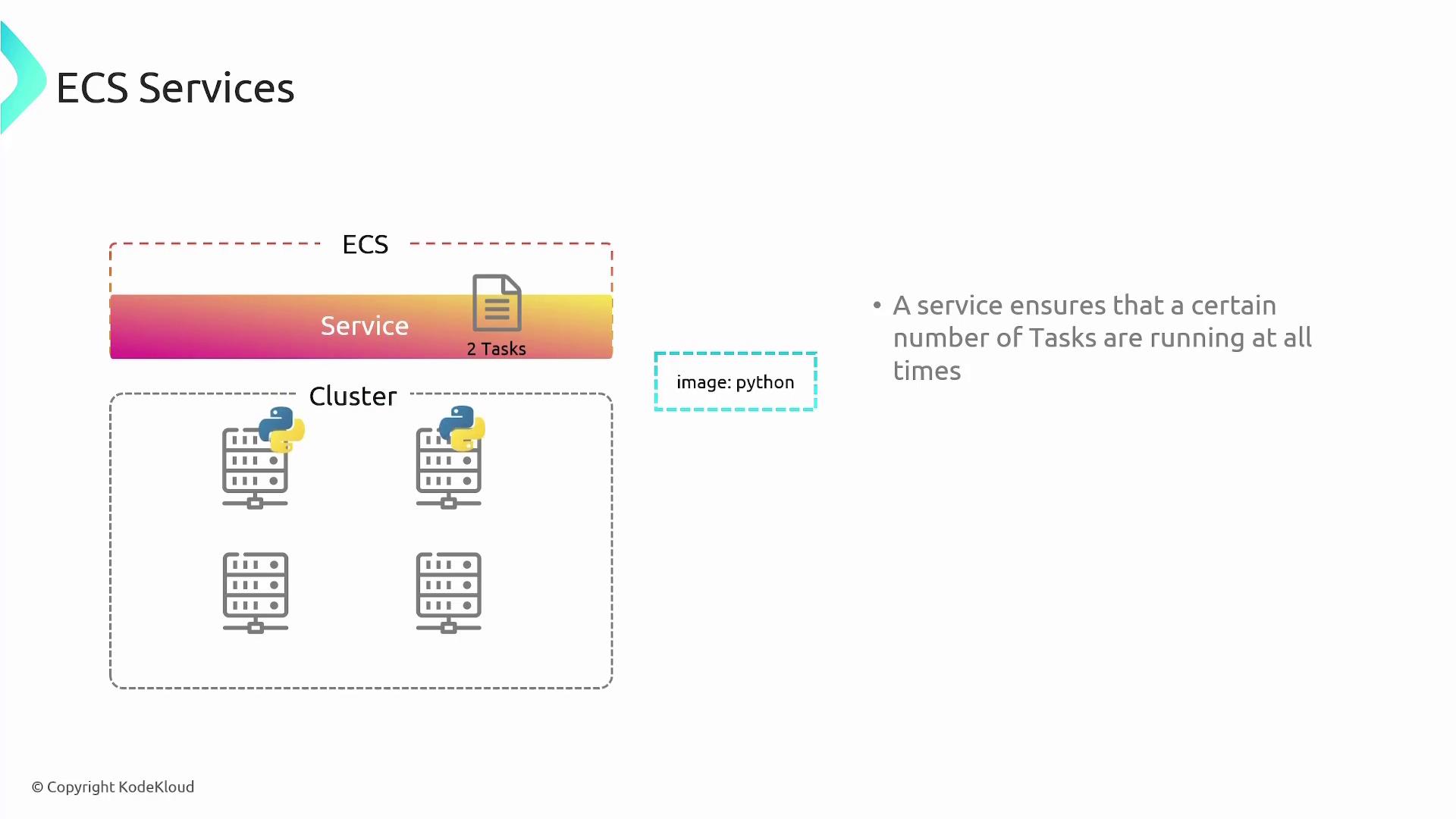
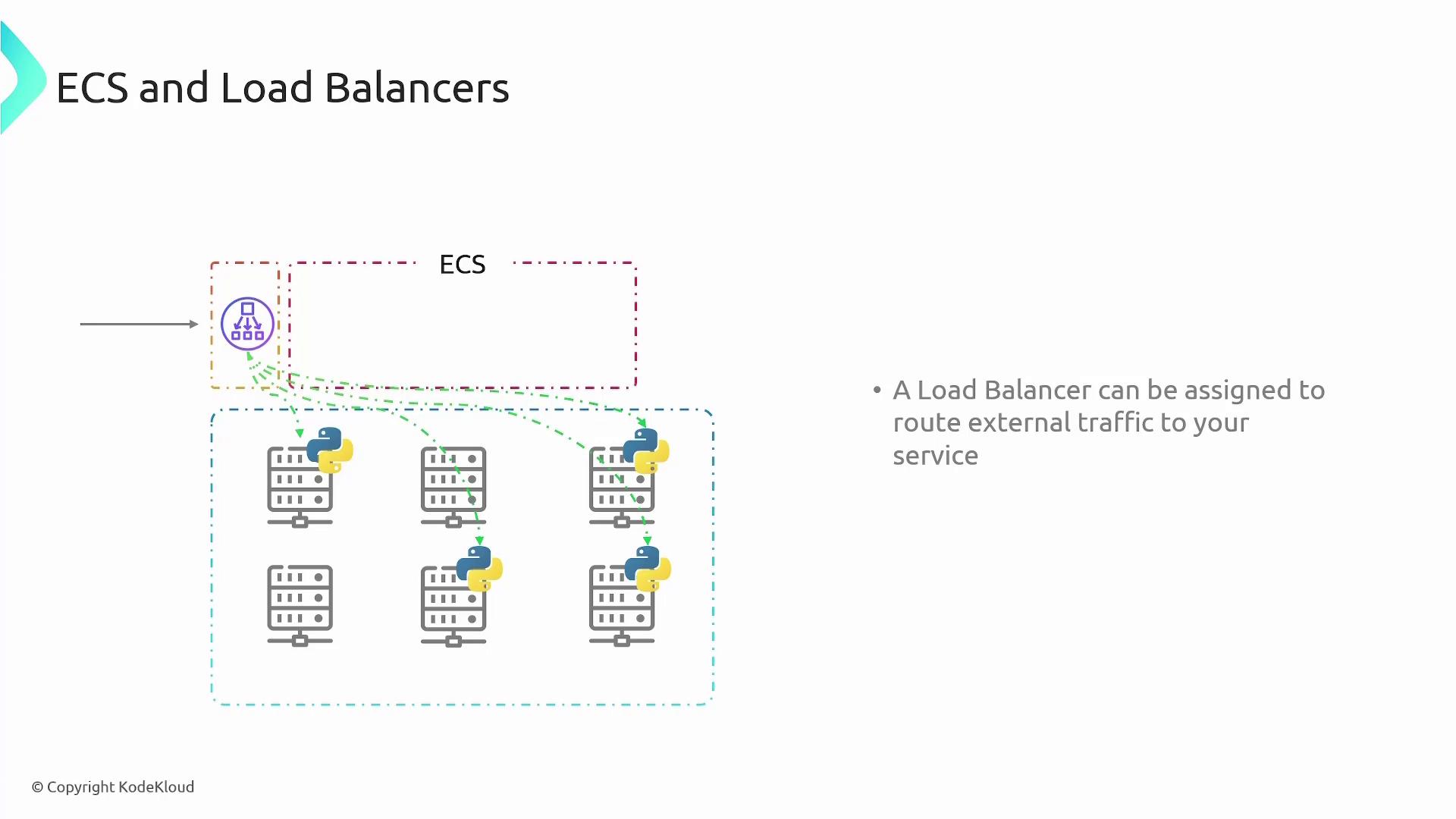
Load Balancers in ECS
Implementing load balancing is essential when deploying multiple container tasks across several hosts. AWS Elastic Load Balancers (ELB) are commonly used to distribute incoming traffic evenly across all available container instances. The load balancer performs the following functions:- Receives incoming requests
- Forwards the requests to the appropriate container tasks
- Dynamically adjusts as new containers are added or removed
This lesson has provided a comprehensive overview of container basics, the challenges associated with containers, and how AWS ECS simplifies container orchestration using both EC2 and Fargate launch types. Additionally, you learned about ECS tasks, task definitions, services, and the critical role of load balancers in managing your containerized applications.