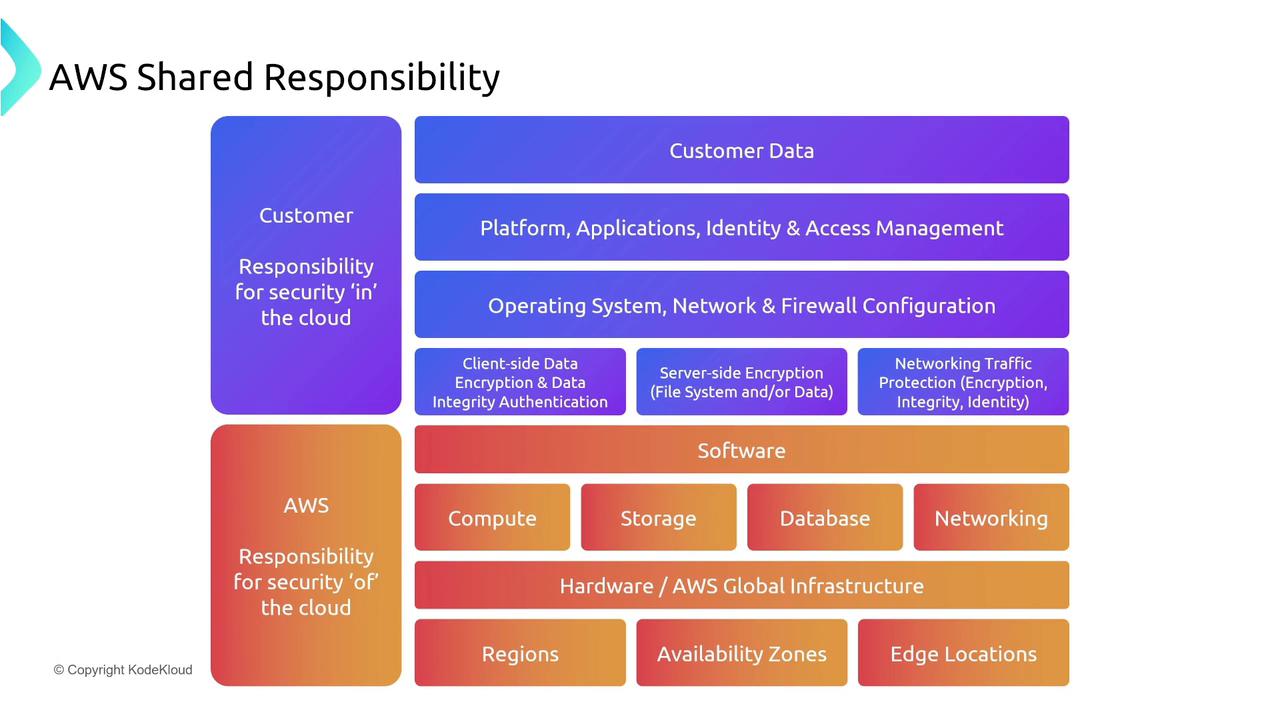
The Shared Responsibility Model
For the Solutions Architecture Associate exam, it is important to understand that while AWS manages much of the underlying infrastructure, you are responsible for key aspects such as application architecture, change management, and failure response. AWS takes care of foundational services like EC2 (infrastructure as a service) and RDS (platform as a service), allowing you to interact with managed services. For instance, while you can adjust parameters on an RDS instance, services like DynamoDB are fully managed via API calls without direct server access.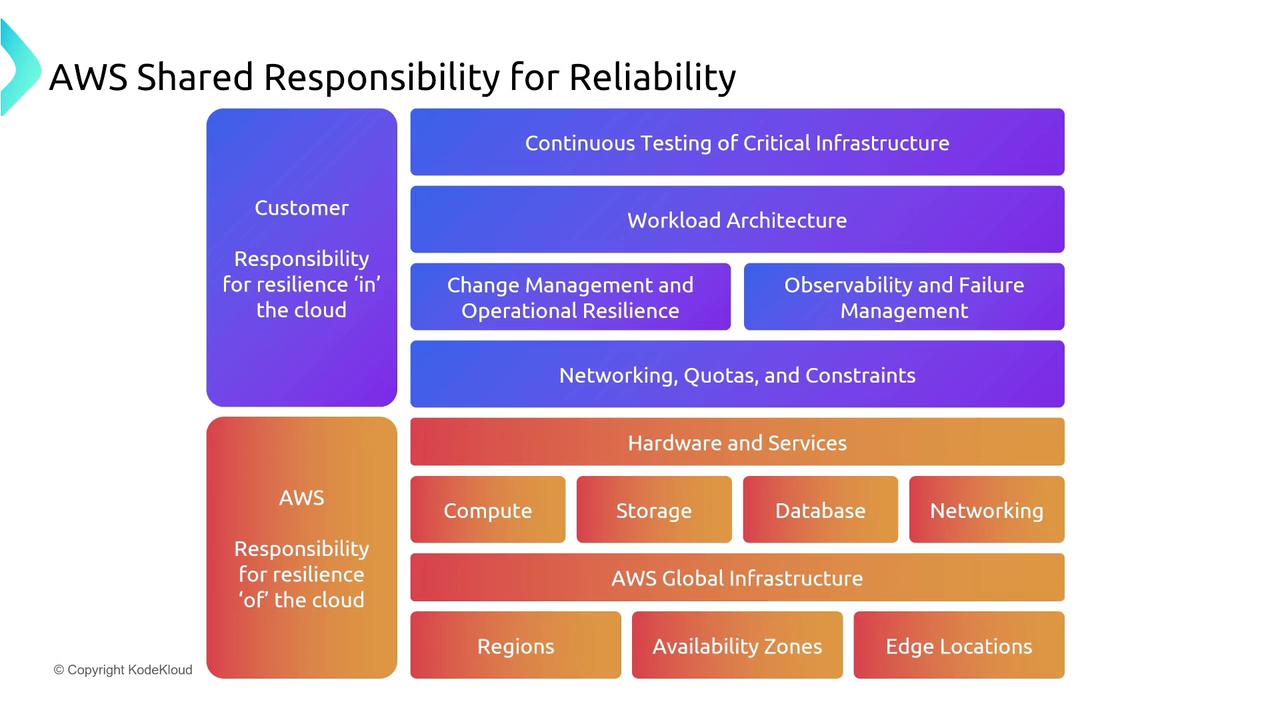
Areas of Focus
Below are four critical areas to consider while designing resilient systems:-
Infrastructure Architecture
Ensure that components like networking, storage, and connectivity are designed with redundancy and resilience in mind. Cloud workloads incorporate service quotas (or service limits) to avoid accidental overuse. Understanding these limits for AWS or third-party services is essential. Resistant architectures commonly feature redundant communication paths and efficient IP address management, as outlined in the Well-Architected Framework. For example, AWS storage services often maintain multiple copies of your data. Services like Aurora might store up to six copies to reinforce reliability. -
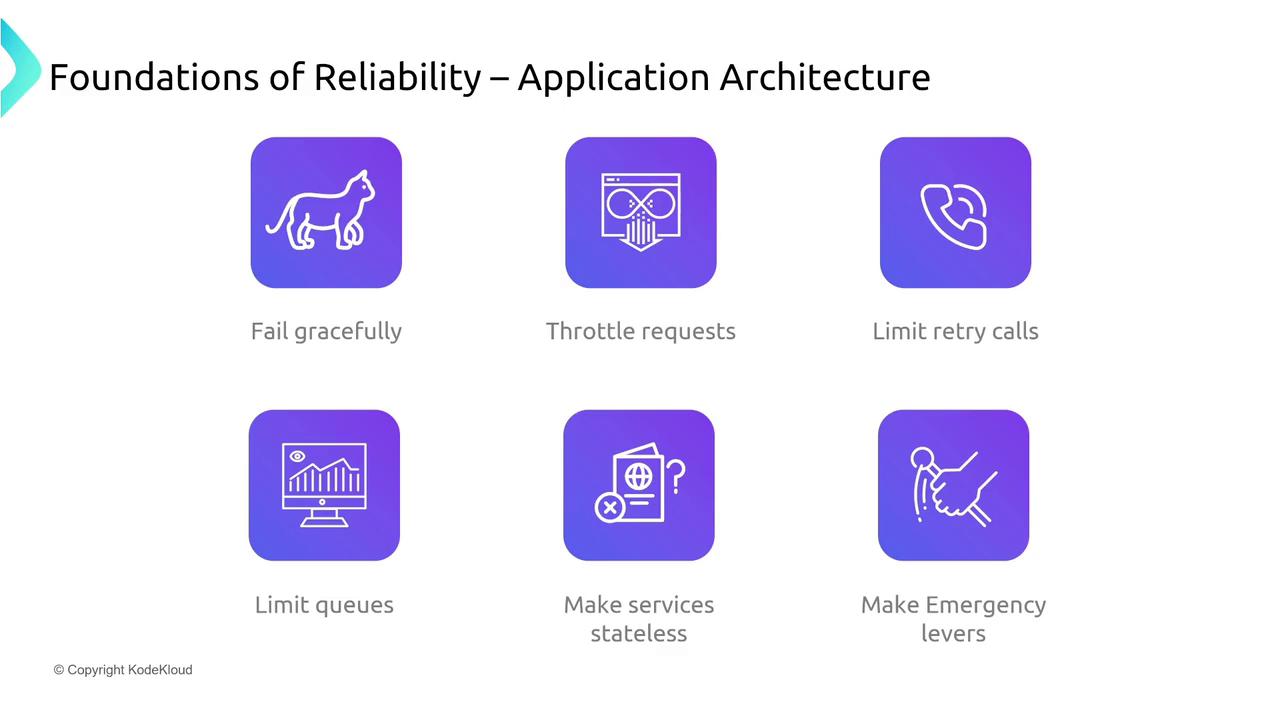
Application (Service) Architecture
Design your applications to be distributed and resilient. A microservices architecture can ensure that a failure in one component does not bring down the entire system. Define clear service contracts through APIs, SLAs, and SLOs to formalize how components interact. Strategies to improve reliability include:- Implementing graceful degradation to maintain service during partial failures.
- Using idempotent operations and rate limiting to prevent cascading issues.
- Applying automatic retry strategies with exponential backoff to handle temporary service endpoint failures.
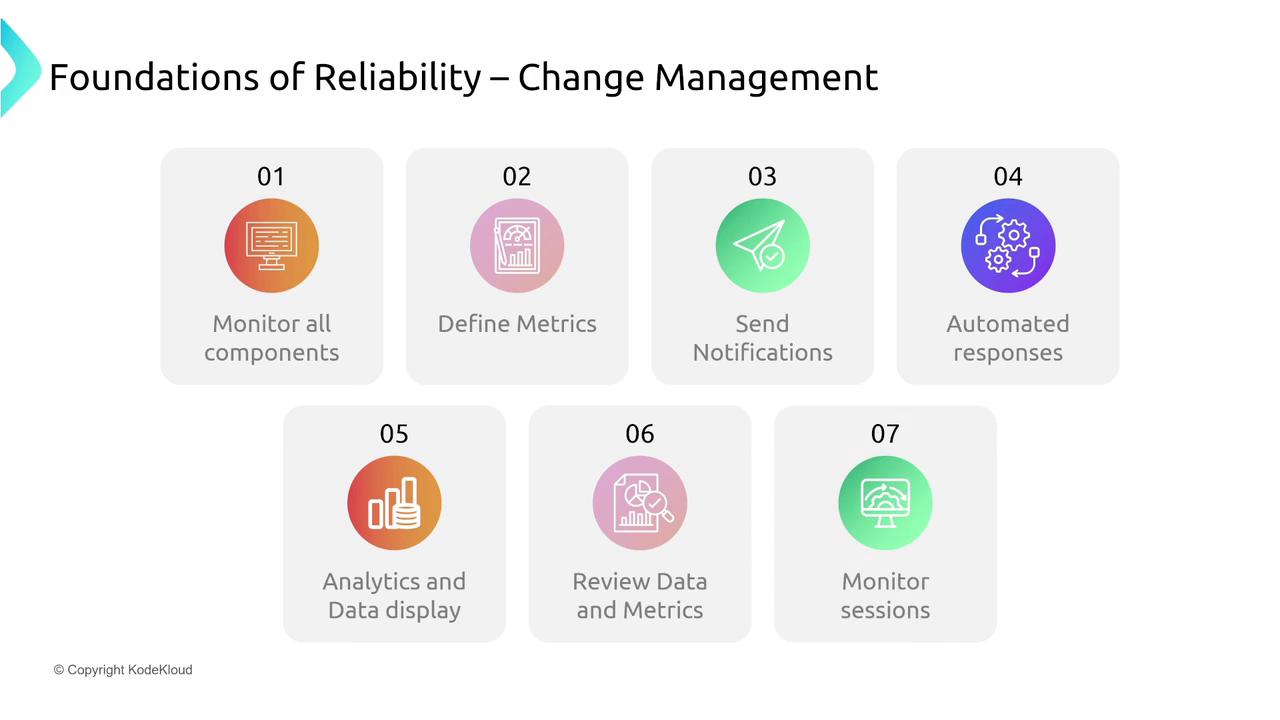
- Change Management
Reliable systems rely on robust change management practices. This includes continuous monitoring of system metrics, automatically scaling resources based on demand, and setting up proactive notifications to flag unexpected changes. Regular load testing, isolating changes to individual components, and automating deployment, testing, and rollback processes are key.

- Failure Management
Even with robust AWS infrastructure, you must have a plan to handle application-level failures. This involves regular backups, automated restoration processes, and continuous testing of your disaster recovery plans. Techniques such as Chaos Engineering or “game days” can be effective for simulating failures and verifying recovery strategies.
Designing resilient systems requires balancing between AWS-managed infrastructure and your application’s unique configuration and response strategies.
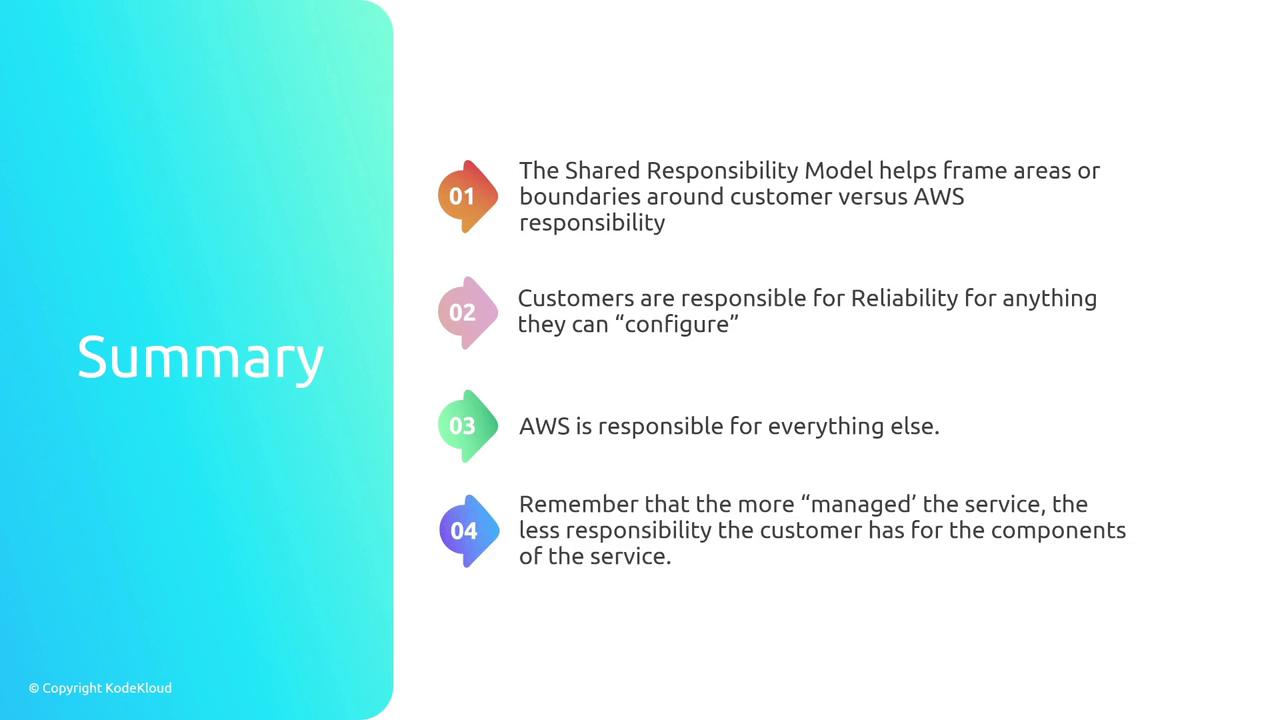
Summary
The AWS Shared Responsibility Model clearly splits roles: AWS manages the underlying infrastructure, while you are accountable for your application’s reliability through strategic design in infrastructure, application architecture, change management, and failure management. As the level of managed services increases, direct responsibility for reliability decreases, but understanding these components remains crucial for building resilient systems.